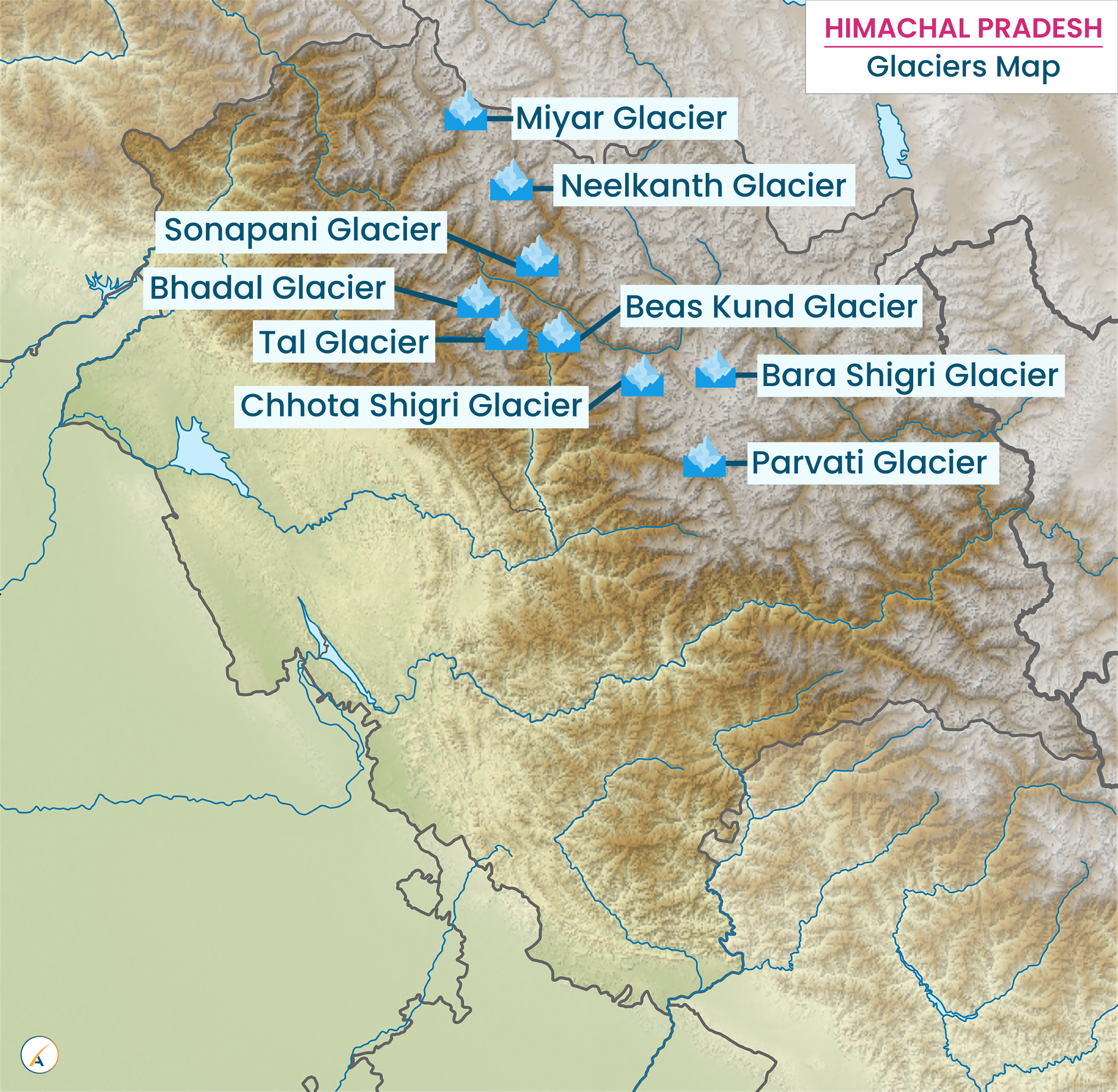
Glaciers in Himachal Pradesh
What is a Glacier?
A glacier is a large body of ice that forms on land through the recrystallization of snow under specific conditions. Essential conditions for glacier formation include:
- Accumulation Zone: A distinct area where more snow or ice accumulates than melts.
- Ablation Zone: A distinct area where more snow or ice melts or wastes than accumulates.
- Movement: A slow transfer or movement of the ice mass from the accumulation zone to the ablation zone.
Glaciers in Himachal Pradesh
Glaciers exhibit a variety of forms and characteristics. Major types include:
- Cliff and Cirque Glaciers
- Continental Ice Sheets
- Valley Glaciers
In the local Himachali language, glaciers are known as “Shigri.” The largest glacier in Himachal Pradesh is Bara Shigri, located in the Chandra Valley of Lahaul, and feeding the River Chenab.
Major Concentrations of Glaciers in Himachal Pradesh
- Bara Banghal: Lies amidst Kangra, Kullu, Chamba, and Lahaul valleys, feeding the River Ravi.
- Lahaul-Spiti and Kullu Valleys: Feeding glacial tributaries of the River Beas.
- Tri-junction of Kullu, Kinnaur, and Spiti: Feeding tributaries of the River Beas and Satluj.
- Chandra Valley: Located in Lahaul.
District-wise Distribution of Glaciers
- Glaciers in Lahaul-Spiti: Bara Shigri, Chhota Shigri, Pacha, Kulti, Shipting, Ding Karmo, Tapn, Gyephang (also known as Manimahesh of Lahaul), Shili, Shamundri, Bolunag, Taragiri, Chandra, Bhaga, Kugti, Lainghar, Doksha, Nilkanth, Milang, Mukkila or Mukkiya, Miyar, Lady of Keylong, Gangstang, Perad, Sonapani, Gora, Takdung, Manthora, Karpat, Ulthampu, and Tharong.
- Glaciers in Kangra: Bhadal.
- Glaciers in Kullu: Parvati, Dudhon, and Beas Kund.
- Glaciers in Shimla: Chandra Nahan.
Other Important Information about Glaciers in Himachal Pradesh
- Most glaciers in Himachal Pradesh are located in the Greater Himalayas.
- Bara Shigri Glacier in Lahaul feeds the Chandra River and is located in the Chandra River Valley, with dimensions of 25 km by 3 km.
- Captain Harcourt conquered the Shigri glacier in 1869 AD.
- Stephenson trekked the Bara Shigri glacier in 1858 AD.
- In 1970 AD, Major Baljit Singh of the Indian Army scaled the Bara Shigri glacier.
- Walker and E.H. Pascoe were part of the Geological Survey team that visited the Bara Shigri glacier in 1906 AD.
- The Himalayan mountain system has over 5,000 glaciers, with approximately 2,500 located in the Himachal Himalayas.
- The Lady of Keylong Glacier is named for a dark patch resembling a female figure carrying a load, named by Lady Elashainghday.
- Andrew Wilson, a European traveler, referred to Lahaul in 1873 AD as ‘The Valley of Glaciers.’
- The Snow and Avalanche Studies Establishment (SASE), a wing of the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), is located in Manali.
- Sonapani Glacier was first surveyed by Walker & Pascoe in 1906 AD.
- Sonapani and Gyephang Glaciers are visible from the Ridge ground in Shimla.
Individual Glacier Details
- Chandra Glacier: Located in the Lahaul-Spiti region, distinct from Bara Shigri, and feeds the River Chandra. It plays a key role in forming Chandratal, a beautiful high-altitude lake.
- Gangstang Glacier: Situated at the western border of the Lahaul region at an altitude of about 5,480 meters. It streams into Shahsha Nullah, which joins the Chandrabhaga River about 13 km to the south.
- Sonapani Glacier: Visible from the Rohtang Pass, features a desiccated lake about 2.5 km long and is approximately 11 km long. It includes an ice-cliff mostly covered by stone, with the glacier stream issuing from an ice cave on the western limb of the curved ice-cliff.
- Perad Glacier: A small and easily accessible glacier located within one kilometer of Putiruni. It has a well-marked ice-cave, and the glacier stream flows between two large lateral moraines.
- Lady of Keylong Glacier: Perched at an elevation of 6,061 meters in Lahaul-Spiti, with year-round snow cover. It resembles a lady and adds a touch of mystique to Himachal’s icy landscapes.
- Bhadal Glacier: Located on the southwestern slopes of the Pir Panjal Range in the Bara Banghal area of Kangra, feeding the Bhadal River.
Glaciers in Himachal Pradesh
The Himalayas, encompassing nearly 15,000 glaciers, is one of the largest ice-covered regions in the world, with about 34,000 square kilometers of ice coverage. Himalayan glaciers play a crucial role in regulating river flows, especially during the monsoon season, by providing water to areas where rainfall is insufficient. They also contribute to seasonal flooding by boosting river levels during the melting phase.
Key Glaciers in Himachal Pradesh
1. Bara Shigri Glacier
- Location: Chandra Valley, Lahaul
- Dimensions: Over 25 km long and about 3 km wide
- Feeding River: Chenab
- Features: Bara Shigri is the largest glacier in Himachal Pradesh, situated in the Chandra Valley. It is flanked by high mountains on three sides and supported by several smaller tributary glaciers. The glacier was instrumental in forming Chandertal Lake following a significant event in 1936. Notably, it was successfully conquered by an all-women mountaineering team in 1956. Other significant glaciers in the Chandra Valley include Chhota Shigri (Small Glacier), Kulti, Shpting, Pacha, Ding Karmo, Tapn, Gyephang, Bolunag, Shili, and Shamundri. Gyephang Glacier, named after the chief deity of the Lahaul Valley, remains snow-covered throughout the year and is regarded as the Manimahesh of Lahaul.
2. Chandra Glacier
- Location: Lahaul-Spiti District
- Feeding River: Chandra River
- Features: Chandra Glacier is separated from Bara Shigri and is the source of Chandertal Lake, also known as the ‘Lake of the Moon.’ The lake, surrounded by snow and scree, has a circumference of 2.5 km and remains frozen during winter.
3. Chandra Nahan Glacier
- Location: South-Eastern slopes of the Himalayas, North-West of Rohru
- Feeding River: Pabbar River
- Features: This glacier, aided by several smaller tributary glaciers, features the Chandra Nahan Lake, accessible only to experienced trekkers. The glacier is elevated over 6,000 meters and is surrounded by towering peaks.
4. Bhadal Glacier
- Location: South-Western slopes of the Pir Panjal range, Bara Banghal area, Kangra District
- Feeding River: Bhadal River
- Features: The Bhadal Glacier’s size increases due to rapid and heavy snowfall. Its catchment area includes U-shaped valleys, waterfalls, moraines, and towering peaks. The Bhadal River is a primary tributary of the Ravi River.
5. Bhaga Glacier
- Location: Lahaul
- Feeding River: Bhaga River
- Dimensions: Approximately 25 km long
- Features: Bhaga Glacier is characterized by U-shaped valleys, waterfalls, and moraines. The glacier, which is devoid of vegetative cover, experiences increased discharge during the summer due to snowmelt. It is surrounded by high, snow-clad peaks.
Additional Notable Glaciers
6. Lady of Keylong Glacier
- Location: Keylong
Location and Features:
The Lady of Keylong Glacier is situated in the Lahaul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, India. Perched atop Tinno village, this glacier stands at a formidable altitude of 20,050 feet. Its prominence makes it clearly visible from the nearby town of Keylong. The glacier is distinctive for a dark patch in its center, which resembles a woman carrying a load on her back. This striking feature is so significant that it remains visible even when covered in snow, earning the glacier its evocative name. Officially recognized by the Geological Survey of India, the glacier’s unique appearance and location add to its allure and significance.
Where is the Lady of Keylong Glacier located?
- A) Lahaul and Spiti district, Himachal Pradesh
- B) Kullu district, Himachal Pradesh
- C) Leh-Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir
- D) Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand
Answer: A) Lahaul and Spiti district, Himachal Pradesh
What is the altitude of the Lady of Keylong Glacier?
- A) 6,000 meters
- B) 6,061 meters
- C) 6,500 meters
- D) 5,500 meters
Answer: B) 6,061 meters
The Lady of Keylong Glacier is named after which distinct feature?
- A) A large rock formation
- B) A dark patch resembling a woman carrying a load
- C) A unique snow formation
- D) A specific plant species
Answer: B) A dark patch resembling a woman carrying a load
What is the approximate height of the peak where the Lady of Keylong Glacier is located?
- A) 15,000 feet
- B) 18,000 feet
- C) 20,050 feet
- D) 22,000 feet
Answer: C) 20,050 feet
How long does a typical expedition to climb the Lady of Keylong Glacier last?
- A) 5 days and 4 nights
- B) 7 days and 6 nights
- C) 11 days and 10 nights
- D) 14 days and 13 nights
Answer: C) 11 days and 10 nights
What is the range of temperatures experienced on the Lady of Keylong Glacier?
- A) -10°C to 15°C
- B) -20°C to 20°C
- C) -17°C to 18°C
- D) -5°C to 10°C
Answer: C) -17°C to 18°C
In what year did a team of 19 mountaineering instructors successfully reach the summit of the Lady of Keylong Glacier?
- A) 2015
- B) 2016
- C) 2017
- D) 2018
Answer: D) 2018
Which village provides a view of the Lady of Keylong Glacier?
- A) Manali
- B) Kullu
- C) Tinno
- D) Keylong
Answer: D) Keylong
The Lady of Keylong Glacier is known for which of the following?
- A) Its large ice caves
- B) Its dark patch that resembles a figure
- C) Its proximity to a large glacier lake
- D) Its relatively warm temperatures
Answer: B) Its dark patch that resembles a figure
What notable organization has officially recognized the Lady of Keylong Glacier?
- A) Indian Mountaineering Foundation
- B) Geological Survey of India
- C) Himalayan Explorers Association
- D) Indian Tourism Board
Answer: B) Geological Survey of Indi
7. Mukkila Glacier
- Location: Bhaga Valley
- Elevation: Approximately 6,478 meters
- Features: Known for its impressive appearance and high elevation, Mukkila Glacier offers stunning views.
8. Sonapani Glacier
- Location: Visible from Rohtang Pass
- Dimensions: About 6 km from the confluence of Kulti Nala
- Features: First surveyed by Walker and Pascoe in 1906, Sonapani Glacier is noted for its visibility and location near the Rohtang Pass.

9. Gora Glacier
- Location: South-facing slopes of the main Himalayan range
- Features: Gora Glacier has receded recently due to an unstable mass balance. It is known for its challenging terrain.
10. Perad Glacier
- Location: Near Putiruni
- Features: A small and accessible glacier, Perad is notable for its proximity to a cave.
11. Parbati and Dudhon Glaciers
- Location: Kullu District
- Dimensions: Both glaciers are about 15 km long
- Feeding River: Parbati River
12. Beas Kund Glacier
- Location: South-facing slopes of Pir Panjal, near Rohtang Pass
- Feeding River: Beas River
- Features: Beas Kund Glacier is a significant source of the Beas River and is located near the famous Rohtang Pass.

1. What is a glacier? A) A large body of water
B) A large body of ice
C) A landform made of sand
D) A type of volcanic rock
Answer: B) A large body of ice
2. What is the term for the area where more snow or ice accumulates than melts? A) Ablation Zone
B) Accumulation Zone
C) Melt Zone
D) Formation Zone
Answer: B) Accumulation Zone
3. Which is the largest glacier in Himachal Pradesh?
A) Chandra Glacier
B) Gangstang Glacier
C) Sonapani Glacier
D) Bara Shigri Glacier
Answer: D) Bara Shigri Glacier
4. In which valley is the Bara Shigri Glacier located? A) Kullu Valley
B) Chandra Valley
C) Spiti Valley
D) Kangra Valley
Answer: B) Chandra Valley
5. What is the local Himachali word for glacier? A) Shila
B) Shigri
C) Shira
D) Sagara
Answer: B) Shigri
6. Which glacier is distinct from Bara Shigri and feeds the River Chandra? A) Sonapani Glacier
B) Gangstang Glacier
C) Chandra Glacier
D) Perad Glacier
Answer: C) Chandra Glacier
7. What major river is fed by the Gangstang Glacier? A) Chenab River
B) Beas River
C) Chandrabhaga River
D) Ravi River
Answer: C) Chandrabhaga River
8. Which glacier is known for its desiccated lake and old terminal moraine visible from Rohtang Pass? A) Perad Glacier
B) Sonapani Glacier
C) Bara Shigri Glacier
D) Chandra Glacier
Answer: B) Sonapani Glacier
9. What is the elevation of the Lady of Keylong Glacier? A) 5,000 meters
B) 5,500 meters
C) 6,061 meters
D) 6,500 meters
Answer: C) 6,061 meters
10. Which glacier is located within one kilometer of Putiruni? A) Sonapani Glacier
B) Perad Glacier
C) Gangstang Glacier
D) Chandra Glacier
Answer: B) Perad Glacier
11. Which district in Himachal Pradesh has the largest concentration of glaciers? A) Kangra
B) Kullu
C) Shimla
D) Lahaul-Spiti
Answer: D) Lahaul-Spiti
12. Which glacier is known for feeding the Bhadal River? A) Bara Shigri Glacier
B) Gangstang Glacier
C) Bhadal Glacier
D) Chandra Glacier
Answer: C) Bhadal Glacier
13. What notable feature is present in the Sonapani Glacier? A) A large terminal moraine
B) An ice cave
C) A high-altitude lake
D) A volcanic crater
Answer: B) An ice cave
14. Which explorer scaled the Bara Shigri Glacier in 1970 AD? A) Captain Harcourt
B) Major Baljit Singh
C) Stephenson
D) Walker & E.H. Pascoe
Answer: B) Major Baljit Singh
15. Which river is fed by the glacier located at the western border of the Lahaul region? A) Chenab River
B) Ravi River
C) Beas River
D) Chandrabhaga River
Answer: D) Chandrabhaga River
16. Which glacier is also known as Manimahesh of Lahaul? A) Gyephang Glacier
B) Perad Glacier
C) Sonapani Glacier
D) Chandra Glacier
Answer: A) Gyephang Glacier
17. Who referred to Lahaul as ‘The Valley of Glaciers’ in 1873 AD? A) Captain Harcourt
B) Andrew Wilson
C) Major Baljit Singh
D) Stephenson
Answer: B) Andrew Wilson
18. Which glacier is visible from the Ridge ground in Shimla? A) Perad Glacier
B) Gangstang Glacier
C) Sonapani Glacier
D) Gyephang Glacier
Answer: C) Sonapani Glacier
19. In which valley is the Chandra Glacier located? A) Kullu Valley
B) Chandra Valley
C) Kangra Valley
D) Beas Valley
Answer: B) Chandra Valley
20. What is the name of the glacier that was first surveyed by Walker & Pascoe in 1906 AD? A) Sonapani Glacier
B) Bara Shigri Glacier
C) Gangstang Glacier
D) Chandra Glacier
Answer: A) Sonapani Glacier
21. Which glacier feeds the glacial tributaries of the River Beas? A) Bara Shigri Glacier
B) Gangstang Glacier
C) Chandra Glacier
D) Perad Glacier
Answer: A) Bara Shigri Glacier
22. What is the primary feature of the Perad Glacier? A) It has a large ice-cliff
B) It is the largest glacier in the region
C) It has a well-marked ice-cave
D) It feeds multiple rivers
Answer: C) It has a well-marked ice-cave
23. Which glacier is described as having a resemblance to a lady carrying a load? A) Gangstang Glacier
B) Chandra Glacier
C) Lady of Keylong Glacier
D) Bara Shigri Glacier
Answer: C) Lady of Keylong Glacier
24. What notable feature does the Sonapani Glacier have on its snout? A) An ice cave
B) A high terminal moraine
C) A stone-covered ice-cliff
D) A glacial lake
Answer: C) A stone-covered ice-cliff
25. Which glacier is located on the southwestern slopes of the Pir Panjal Range in Kangra? A) Chandra Glacier
B) Perad Glacier
C) Bhadal Glacier
D) Sonapani Glacier
Answer: C) Bhadal Glacier











