Brief Geography of Kinnaur District
जिला किन्नौर: एक संक्षिप्त विवरण
भौगोलिक स्थिति:
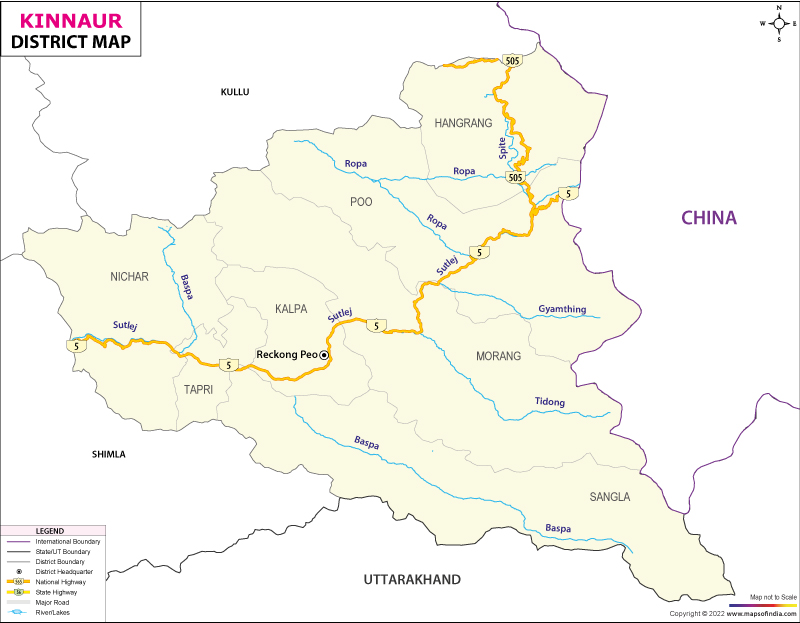
जिला किन्नौर 77°45′ और 79°00’35” पूर्वी देशांतर तथा 31°55’50” और 32°05’15” उत्तरी अक्षांश के बीच स्थित है। किन्नौर हिमाचल प्रदेश के उत्तर-पूर्वी भाग में स्थित है। किन्नौर तिब्बत और ज़ांस्कर पहाड़ों के साथ पूर्वी सीमा साझा करता है और तिब्बत और किन्नौर के बीच अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सीमा बनाता है। यह सीमा “परेछू” नामक बिंदु से शुरू होती है और शिपकिला दर्रे से पूर्व में चोर गाद घाटी तक पहुँचती है। दक्षिण और दक्षिण-पूर्व में उत्तराखंड है, पश्चिम में शिमला जिला है, उत्तर और उत्तर-पश्चिम में लाहौल और स्पीति है, और पश्चिम से कुल्लू इसे छूता है।
मुख्यालय और ऊंचाई:
- मुख्यालय: रिकांगपिओ
- ऊंचाई: 2769 मीटर
बोली जाने वाली भाषाएँ:
- किन्नौरी (हम्सकद)
- संगनौर
- जांगियाम
- शुमेचो
किन्नौर जिले में पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ:
यह जिला तीन प्रमुख पर्वत श्रृंखलाओं से घिरा हुआ है:
- पूर्व में ज़ांस्कर पर्वत
- महान हिमालय: उत्तर-पश्चिम से दक्षिण-पूर्व तक फैला हुआ
- धौलाधार पर्वतमाला: जिले की दक्षिणी सीमा बनाती है
किन्नौर जिले में पर्वत चोटियाँ:
- लियो पार्गियाल: 6816 मीटर (किन्नौर जिले की सबसे ऊंची चोटी)
- राल्डांग
- गुशु
- पिशु
- फवारंग
- जोरकादेन
- किन्नर कैलाश
- परसल
- शिल्पकी
लियो फार्गिल, शिल्ला और पारसल चोटियां ज़ांस्कर श्रेणी में स्थित हैं, जबकि राल्डांग और किन्नर कैलाश वृहत्तर हिमालय में स्थित हैं।
Brief Geography of Kinnaur District किन्नौर जिले में ग्लेशियर:
- पश्चिमी किन्नौर वृहद हिमालय:
- संकरिशुल
- माना दानी
- ड्रिमिलिंग
- फूलढांग
- जांगसू
- धौलाधार:
- हनिया
- बिलारे
- पूर्वी किन्नौर ग्रेटर हिमालय:
- सारो ग्लेशियर
- गारा ग्लेशियर
- लांबर ग्लेशियर
Brief Geography of Kinnaur District किन्नौर जिले की महत्वपूर्ण घाटियाँ:
- सतलुज घाटी:
- यह सतलुज नदी द्वारा प्रवाहित जिले की सबसे बड़ी घाटी है
- हंगरंग घाटी (स्पीति घाटी):
- जल निकास स्पीति या ली नदी द्वारा होता है
- यह घाटी खाब गांव के पास सतलुज घाटी से मिलती है
- निचला भाग किन्नौर में और ऊपरी भाग लाहौल स्पीति में स्थित है
- बस्पा या सांगला घाटी:
- जल निकास बास्पा नदी द्वारा होता है
- सांगला गांव के नाम पर इसका नाम सांगला घाटी पड़ा
- ऐतिहासिक गांव कामरू (बुशहर राज्य की पुरानी राजधानी) इसी घाटी में स्थित है
- यह घाटी बारूस दर्रा, किमल्या दर्रा, बोरसू दर्रा और लमखंगा दर्रा द्वारा उत्तराखंड के गढ़वाल क्षेत्र से जुड़ी हुई है
- चित्तकुल गांव:
- बसपा घाटी का अंतिम और सबसे ऊंचा गांव
- भारत-तिब्बत सीमा के पास अंतिम बसा हुआ गांव
- भारत में यह एक ऐसा स्थान है जहां बिना परमिट के यात्रा की जा सकती है
- चित्तकुल के आलू दुनिया के सर्वोत्तम आलू में से एक हैं
- अन्य प्रमुख घाटियाँ:
- युला घाटी
- मुलगांव घाटी
- रोपा या श्यासो या सुनाम घाटी
- टीडोंग घाटी
- वांगपू या भाबा घाटी
- ग्याथिंग या नेसांग घाटी
- पेजुर या लिप्पा घाटी
- काशांग घाटी
- रिब्बा घाटी
जिला किन्नौर की नदी प्रणाली:
- सतलुज नदी: किन्नौर को दो बराबर भागों में विभाजित करती है
सतलुज की सहायक नदियाँ:
- स्पीति नदी: यह स्पीति से निकलती है और फिर किन्नौर में प्रवेश करती है। यह किन्नौर की दूसरी प्रमुख नदी है और खाब गांव में सतलुज नदी से मिलती है
- बास्पा
- जुपकिया
- थाटांग
- बेरिंग
- रुतकी
- शुथी
रोपा नदी: किन्नौर जिले और लाहौल-स्पीति के बीच की सीमा पर उत्पन्न होती है और “शाशो” के पास सतलुज में मिल जाती है
- पेजुर
- तैती
- युला
Brief Geography of Kinnaur District जिला किन्नौर में झीलें:
- नाको झील: हंगरंग तहसील में
- सोरंग झील: निचार तहसील के जानी और रामनी गांव के ऊपर
- टेम्चो/थेम-त्सो झील: संभवतः पू तहसील
किन्नौर जिले में झरने:
- नाथपा
- टापरी
- जोकटियारिंग
अन्य जानकारी:
- भाभा: किन्नौर जिले का सबसे बड़ा गांव
- टिडोंग घाटी: ‘जंगली भव्यता का दृश्य’
- रिब्बा घाटी: अंगूर के लिए प्रसिद्ध
जिला किन्नौर में प्राकृतिक वनस्पति:
किन्नौर में तीन प्रकार की प्राकृतिक वनस्पतियाँ हैं:
- आर्द्र क्षेत्र वन: सतलुज घाटी के बाईं ओर पाया जाता है। इसमें कैल, स्प्रूस, फर, चेस्टनट, मेपल, बर्ड चेरी और अखरोट शामिल हैं
- शुष्क क्षेत्र के जंगल: निचार से चीनी तक पाए जाते हैं। इसमें देवदार, नीला चीड़, स्प्रूस, सिल्वर फर और निओज़ा चीड़ (भारत में एकमात्र निओज़ा जंगल) शामिल हैं
- शुष्क क्षेत्र वन: तिब्बती सीमा से सटे इलाकों में पाया जाता है। इसमें रोज़ डॉग और ड्वार्फ झाड़ियाँ शामिल हैं
जिला किन्नौर में खनिज:
- रांवर और रोपा के पास: तांबा
- छागांव के पास: चांदी
- शैलखार और छगांव में: जिप्सम
- सांगला घाटी में: खुरदरी स्लेट
- असरंग और लिप्पा क्षेत्र में: चीनी मिट्टी
- तांगलिंग खड्ड में: अभ्रक
Geographic Position:
Kinnaur district is located between 77°45′ and 79°00’35” eastern longitude and 31°55’50” and 32°05’15” northern latitude. Kinnaur is situated in the northeastern part of Himachal Pradesh. It shares its eastern boundary with Tibet and the Zanskar Range, forming the international border between Tibet and Kinnaur. This border starts from a point called “Parekchu” and extends eastward to the Choro Gad Valley near the Shipkila Pass. To the south and southeast lies Uttarakhand, to the west is the Shimla district, to the north and northwest is Lahaul and Spiti, and to the west, it touches Kullu.
Headquarters and Elevation:
- Headquarters: Reckong Peo
- Elevation: 2769 meters
Languages Spoken:
- Kinnauri (Hamskad)
- Sanglaur
- Jangiyam
- Shumecho
Mountain Ranges in Kinnaur District:
The district is surrounded by three major mountain ranges:
- Zanskar Range: To the east
- Great Himalayas: Extending from northwest to southeast
- Dhauladhar Range: Forms the southern boundary of the district
Mountain Peaks in Kinnaur District:
- Leo Pargial: 6816 meters (Highest peak in Kinnaur district)
- Raldang
- Gushu
- Pishu
- Fawarang
- Jorkaden
- Kinner Kailash
- Parsel
- Shilpki
Leo Pargial, Shilla, and Parsel peaks are located in the Zanskar range, while Raldang and Kinner Kailash are situated in the Greater Himalayas.
Glaciers in Kinnaur District:
Western Kinnaur Greater Himalayas:
- Sankarshul
- Mana Dani
- Drimiling
- Phooldhang
- Jangsu
Dhauladhar:
- Hania
- Bilare
Eastern Kinnaur Greater Himalayas:
- Saro Glacier
- Gara Glacier
- Lamber Glacier
Important Valleys in Kinnaur District:
- Satluj Valley: The largest valley in the district, drained by the Satluj River.
- Hungerang Valley (Spiti Valley): Drained by the Spiti or Li River. This valley meets the Satluj Valley near the village of Khab. The lower part is in Kinnaur, and the upper part is in Lahaul Spiti.
- Baspa or Sangla Valley: Drained by the Baspa River. Named after the village of Sangla. The historic village of Kamru (the old capital of Bushahr state) is located in this valley. It is connected to the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand by the Baruas Pass, Kimlya Pass, Borsu Pass, and Lamkhanga Pass.
- Chitkul Village: The last and highest village of the Baspa Valley. The last inhabited village close to the India-Tibet border. It is a place where travel is possible without a permit. The potatoes of Chitkul are among the best in the world.
Other Major Valleys:
- Yula Valley
- Mulgow Valley
- Ropa or Shyaso or Sunam Valley
- Tiding Valley
- Wangpo or Bhabha Valley
- Gyathing or Nesang Valley
- Pejur or Lippa Valley
- Kashang Valley
- Ribba Valley
River System in Kinnaur District:
- Satluj River: Divides Kinnaur into two equal parts.
Tributaries of the Satluj River:
Spiti River: Originates from Spiti and then enters Kinnaur. It is the second major river in Kinnaur and joins the Satluj River at Khab village.
Baspa
Jupakia
Thatang
Bering
Rutki
Shuthi
Ropa River: Originates at the border between Kinnaur and Lahaul-Spiti and joins the Satluj River near “Shasho”.
Other Tributaries:
- Pejur
- Taity
- Yula
Lakes in Kinnaur District:
- Nako Lake: Located in the Hungerang Tehsil.
- Sorang Lake: Situated above the Jani and Ramni villages in Nichar Tehsil.
- Temcho/Them-Tso Lake: Possibly located in the Pooh Tehsil.
Waterfalls in Kinnaur District:
- Nathpa
- Tapri
- Joktiaring
Other Information:
- Bhaba: The largest village in Kinnaur district.
- Tiding Valley: Known for its ‘wild grandeur.’
- Ribba Valley: Famous for its grapes.
Natural Vegetation in Kinnaur District:
Kinnaur has three types of natural vegetation:
- Moist Area Forests: Found to the left of the Satluj Valley. Includes Kail, Spruce, Fir, Chestnut, Maple, Bird Cherry, and Walnut.
- Dry Area Forests: Found from Nichar to Chini. Includes Cedar, Blue Pine, Spruce, Silver Fir, and Neozone Pine (the only Neozone forest in India).
- Dry Area Shrubs: Found in areas adjacent to the Tibetan border. Includes Rose Dog and Dwarf Shrubs.
Minerals in Kinnaur District:
- Near Ranwar and Ropa: Copper
- Near Chagao: Silver
- In Shaikhara and Chagao: Gypsum
- In Sangla Valley: Coarse Slate
- In Asrang and Lippa Areas: China Clay
- In Tangling Khad: Mica
Flora and Fauna
Vegetation:
In Kinnaur, the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas are characterized by sparse vegetation consisting mainly of hardy grasses. Alpine species such as juniper, pine, fir, cypress, and rhododendron are found at elevations between 3,500 and 5,000 meters, particularly in Middle Kinnaur. At lower elevations, where the climate is more temperate, the vegetation includes trees such as oak, chestnut, maple, birch, alder, magnolia, apple, and apricot.
Fauna:
In the higher regions, local farmers rear yaks and dzos. Scattered populations of the Himalayan black bear and small ponies can also be observed.
Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary
Overview:
Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary spans an area of 503 square kilometers in the Rupi Bhaba region of Kinnaur. Established in 1982, it originally covered 239 square kilometers of the Bushahr state forests.
Geographical Boundaries:
- North: Encompasses the main Srikhand Dhar, starting from Kokshane Peak.
- East: Covers the ridge line from high points of 5,567 meters on the Srikhand mountain range, extending south. It traverses Nichar from Murang Tehsil, then Kalpa Tehsil, reaching up to the ridge line of Mukim Dhar and the peak of 5,496 meters.
- South: Includes Listrang Gad, Khosyan, Angyar Ghat, Wanger Khad, Soling Dhar, Saknatpa PF, Kandarn Khad, Shorang Khad, and Bara Kamba.
- West: Starts from the high point of 3,038 meters, following the boundaries of Shimla and Kinnaur to Srikhand Dhar via Gushu Pishu Peak, extending up to Kokshane Peak.
Flora:
The sanctuary features diverse plant species including kharsu, oak, weeping fig, alpine plants, chir pine, Himalayan temperate forest species, and both coniferous and broad-leaved coniferous trees.
Fauna:
The wildlife within Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary includes:
- Snow leopard
- Brown bear
- Himalayan tahr
- Blue sheep
- Indian fox
- Musk deer
This rich biodiversity supports a variety of species and makes the sanctuary an important ecological zone in Kinnaur.
Climate
Kinnaur experiences a predominantly temperate climate owing to its high elevation. The climatic conditions are characterized by:
- Winters: Long and lasting from October to May, with temperatures dropping significantly due to the altitude.
- Summers: Short, spanning from June to September, with milder temperatures compared to the winter months.
In the lower parts of Kinnaur, particularly in the Sutlej Valley and the Baspa Valley, the monsoon season brings rainfall. The Baspa Valley receives the highest amount of rainfall in July.
However, the upper regions of these valleys fall into the rain-shadow area, which results in arid conditions similar to the climates of Tibet and Central Asia.
A 2016 study conducted by IIT Delhi found that Kinnaur district has the cleanest air in the country, reflecting its relatively unspoiled environmental conditions.
- किन्नौर जिले के कितने डिग्री पूर्वी देशांतर की सीमा में स्थित है?
A) 77°45′
B) 78°30′
C) 79°00’35”
D) 80°15′
उत्तर: C) 79°00’35”
विवरण: किन्नौर जिले की पूर्वी सीमा 77°45′ और 79°00’35” देशांतर के बीच स्थित है। 79°00’35” इसका अधिकतम पूर्वी देशांतर है, जो सीमा की परिभाषा को सही रूप से व्यक्त करता है।
- किन्नौर जिले का मुख्यालय कौन सा स्थान है?
A) शिमला
B) रिकांगपिओ
C) कुल्लू
D) लाहौल
उत्तर: B) रिकांगपिओ
विवरण: किन्नौर जिले का मुख्यालय रिकांगपिओ है, जो जिले का प्रशासनिक और भौगोलिक केंद्र है। यह ऊँचाई पर स्थित है और जिले का प्रमुख प्रशासनिक स्थल है।
- किन्नौर जिले में सबसे ऊँची चोटी कौन सी है?
A) राल्डांग
B) गुशु
C) लियो पार्गियाल
D) किन्नर कैलाश
उत्तर: C) लियो पार्गियाल
विवरण: लियो पार्गियाल किन्नौर जिले की सबसे ऊँची चोटी है, जिसकी ऊँचाई 6816 मीटर है। यह वृहत्तर हिमालय में स्थित है और किन्नौर की प्रमुख पर्वत चोटी है।
- सतलुज घाटी का जल निकास कौन सी नदी द्वारा होता है?
A) बास्पा
B) स्पीति
C) रोपा
D) सतलुज
उत्तर: D) सतलुज
विवरण: सतलुज घाटी का जल निकास सतलुज नदी द्वारा होता है, जो जिले की सबसे बड़ी घाटी है और किन्नौर को दो हिस्सों में विभाजित करती है।
- किन्नौर जिले के कौन से पर्वत श्रृंखला जिले की दक्षिणी सीमा बनाती है?
A) ज़ांस्कर पर्वत
B) महान हिमालय
C) धौलाधार पर्वतमाला
D) हिमालय
उत्तर: C) धौलाधार पर्वतमाला
विवरण: धौलाधार पर्वतमाला किन्नौर जिले की दक्षिणी सीमा बनाती है। यह पर्वतमाला दक्षिण-पश्चिम हिमाचल प्रदेश में फैली हुई है और किन्नौर की दक्षिणी सीमा पर स्थित है।
- किन्नौर जिले के किस गांव को ‘भारत-तिब्बत सीमा के पास अंतिम बसा हुआ गांव’ कहा जाता है?
A) बस्पा
B) चित्तकुल
C) सांगला
D) शिपकिला
उत्तर: B) चित्तकुल
विवरण: चित्तकुल गांव भारत-तिब्बत सीमा के पास स्थित है और इसे भारत में बिना परमिट के यात्रा करने योग्य अंतिम गांव माना जाता है। यह बसपा घाटी का अंतिम गांव भी है।
- ‘पश्चिमी किन्नौर वृहद हिमालय’ में कौन सा ग्लेशियर नहीं है?
A) संकरिशुल
B) सारो
C) माना दानी
D) फूलढांग
उत्तर: B) सारो
विवरण: सारो ग्लेशियर पूर्वी किन्नौर ग्रेटर हिमालय में स्थित है, जबकि संकरिशुल, माना दानी, और फूलढांग पश्चिमी किन्नौर वृहद हिमालय में स्थित हैं।
- किन्नौर जिले में ‘जांगसु’ किस श्रेणी का ग्लेशियर है?
A) धौलाधार
B) पूर्वी किन्नौर ग्रेटर हिमालय
C) पश्चिमी किन्नौर वृहद हिमालय
D) ज़ांस्कर
उत्तर: C) पश्चिमी किन्नौर वृहद हिमालय
विवरण: ‘जांगसु’ ग्लेशियर पश्चिमी किन्नौर वृहद हिमालय में स्थित है। यह किन्नौर के पश्चिमी भाग में हिमालय के प्रमुख ग्लेशियरों में से एक है।
- किन्नौर जिले के ‘रिब्बा घाटी’ का प्रमुख उत्पाद क्या है?
A) चाय
B) अंगूर
C) धान
D) चांदी
उत्तर: B) अंगूर
विवरण: रिब्बा घाटी अंगूर के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। यहाँ की जलवायु और मिट्टी अंगूर की खेती के लिए उपयुक्त है, और यह स्थानीय उत्पादों में प्रमुख है।
- किन्नौर जिले में ‘नाको झील’ किस तहसील में स्थित है?
A) निचार
B) पू
C) हंगरंग
D) सांगला
उत्तर: C) हंगरंग
विवरण: नाको झील हंगरंग तहसील में स्थित है। यह झील किन्नौर के हंगरंग क्षेत्र में एक प्रमुख जलाशय है और पर्यटकों के लिए आकर्षण का केंद्र है।
किन्नौर जिले की झीलें
नाको झील
- स्थान: हंगरंग तहसील
- विवरण: नाको झील किन्नौर जिले के हंगरंग क्षेत्र में स्थित है। यह झील अपने सुंदर दृश्य और शांत वातावरण के लिए प्रसिद्ध है।
 2. सोरंग झील
2. सोरंग झील- स्थान: निचार तहसील के जानी और रामनी गांव के ऊपर
- विवरण: सोरंग झील किन्नौर जिले के निचार तहसील में स्थित है। यह झील ऊँचाई पर स्थित है और स्थानीय लोगों द्वारा धार्मिक महत्व की मानी जाती है।

टेम्चो/थेम-त्सो झील
- स्थान: पू तहसील
- विवरण: टेम्चो या थेम-त्सो झील पू तहसील के क्षेत्र में स्थित है। यह झील किन्नौर की विभिन्न झीलों में से एक है और अपनी सुंदरता के लिए जानी जाती है।

What is the eastern longitudinal boundary of Kinnaur district?
A) 77°45′
B) 78°30′
C) 79°00’35”
D) 80°15′Answer: C) 79°00’35”
Explanation: The eastern longitudinal boundary of Kinnaur is between 77°45′ and 79°00’35”.What is the headquarters of Kinnaur district?
A) Shimla
B) Reckong Peo
C) Kullu
D) LahaulAnswer: B) Reckong Peo
Explanation: Reckong Peo is the administrative headquarters of Kinnaur district.Which peak is the highest in Kinnaur district?
A) Raldang
B) Gushu
C) Leo Pargial
D) Kinner KailashAnswer: C) Leo Pargial
Explanation: Leo Pargial is the highest peak in Kinnaur, with an elevation of 6816 meters.Which glacier is located in the Western Kinnaur Greater Himalaya?
A) Shankarishul
B) Saru
C) Mana Dani
D) BilerAnswer: A) Shankarishul
Explanation: Shankarishul is a glacier located in the Western Kinnaur Greater Himalaya.Which valley is not a major valley in Kinnaur?
A) Satluj Valley
B) Baspa Valley
C) Chitkul Valley
D) Yula ValleyAnswer: D) Yula Valley
Explanation: The Yula Valley is not listed as a major valley in Kinnaur.What is the primary river flowing through the Satluj Valley?
A) Baspa
B) Spiti
C) Sutlej
D) RaviAnswer: C) Sutlej
Explanation: The Satluj Valley is primarily drained by the Sutlej River.Which valley is known for being the last inhabited village near the India-Tibet border?
A) Baspa Valley
B) Sangla Valley
C) Chitkul
D) Ropa ValleyAnswer: C) Chitkul
Explanation: Chitkul is the last inhabited village near the India-Tibet border.Which glacier is located in the Eastern Kinnaur Greater Himalaya?
A) Saru
B) Shorang
C) Lama
D) RutiAnswer: A) Saru
Explanation: The Saru Glacier is located in the Eastern Kinnaur Greater Himalaya.What is the main feature of the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary’s southern boundary?
A) Srikhand Dhar
B) Listrang Gad
C) Nichar Ridge
D) Mukim DharAnswer: B) Listrang Gad
Explanation: The southern boundary of the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary meanders through Listrang Gad and other areas.Which animal is NOT found in the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary?
A) Snow Leopard
B) Brown Bear
C) Indian Elephant
D) Musk DeerAnswer: C) Indian Elephant
Explanation: The Indian Elephant is not found in the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary.What kind of trees are found in the temperate climate areas of Kinnaur?
A) Juniper and Pine
B) Oak and Chestnut
C) Rhododendron and Cypress
D) Cedar and FirAnswer: B) Oak and Chestnut
Explanation: Temperate climate areas in Kinnaur have trees such as oak, chestnut, and maple.Which valley is associated with the highest rainfall in Kinnaur?
A) Satluj Valley
B) Baspa Valley
C) Sangla Valley
D) Chitkul ValleyAnswer: B) Baspa Valley
Explanation: The Baspa Valley receives the highest rainfall, particularly in July.Which of the following is NOT a major glacier in Western Kinnaur?
A) Shorang
B) Phuldang
C) Sangla
D) JangsuAnswer: C) Sangla
Explanation: Sangla is a valley, not a glacier in Western Kinnaur.Which type of climate is found in the upper areas of Kinnaur?
A) Temperate
B) Arid
C) Tropical
D) SubtropicalAnswer: B) Arid
Explanation: The upper areas of Kinnaur are in the rain-shadow region and have an arid climate.In which district of Himachal Pradesh is the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary located?
A) Kullu
B) Shimla
C) Lahaul and Spiti
D) KinnaurAnswer: D) Kinnaur
Explanation: The Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Kinnaur district.Which of the following species is NOT a part of the fauna in the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary?
A) Himalayan Tahr
B) Blue Sheep
C) Musk Deer
D) TigerAnswer: D) Tiger
Explanation: Tigers are not found in the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary.What is the approximate area of the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary?
A) 239 sq.km
B) 503 sq.km
C) 600 sq.km
D) 750 sq.kmAnswer: B) 503 sq.km
Explanation: The Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary spans approximately 503 square kilometers.Which glacier is located in the Eastern Kinnaur region?
A) Saru
B) Gara
C) Lamber
D) PhuldangAnswer: A) Saru
Explanation: The Saru Glacier is located in Eastern Kinnaur.Which village is known for producing some of the best potatoes in India?
A) Baspa
B) Chitkul
C) Sangla
D) KamruAnswer: B) Chitkul
Explanation: Chitkul is famous for producing some of the best potatoes.Which river flows through the Baspa Valley?
A) Sutlej
B) Baspa
C) Spiti
D) ChenabAnswer: B) Baspa
Explanation: The Baspa Valley is drained by the Baspa River.