Geography Of chamba District: Himachal Pradesh
Brief Geography of Chamba District: An In-Depth Overview
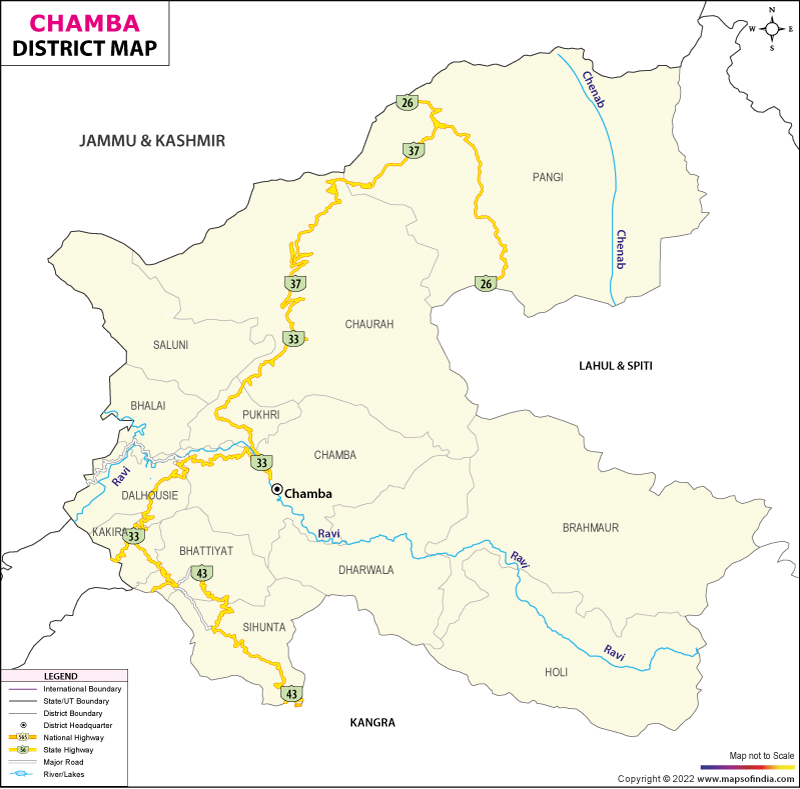
Chamba District, located in the scenic state of Himachal Pradesh, India, is renowned for its stunning geographical diversity. From its lush valleys to its majestic mountain ranges, this region offers a rich tapestry of natural beauty. Here’s an insightful overview of the geography of Chamba District, covering its lakes, rivers, and mountain ranges.
Basic Details
- Capital: Chamba
- Area: 6,528 km²
- Population (2011 Census): 519,080
- Population Density: 80/km²
- Sub-divisions: 7 Tehsils
- Main Languages: Pahari, Hindi
Major Lakes in Chamba District
Chamba District is home to several picturesque lakes that enhance its natural allure. Notable lakes include:
- Ghadassaru Lake
- Khajjiar Lake
- Lama Dal Lake
- Manimahesh Lake (also known as Chaurasi ka Dal or Khundi Maral Lake)
- Chamera Lake (Artificial Lake)
- Mahakali Lake
- Chandrakup Lake
- Chamunda Lake
- Khajund Lake
- Chakund Lake
Lakes in the Dhauladhar Range
- Nagara Lake
- Kali Kund
- Dham Godi
- Kali Dal
- Nag Dal
Lakes of Chamba District: A Comprehensive Overview
Chamba District in Himachal Pradesh is renowned for its diverse and scenic lakes, each adding to the natural beauty of the region. These lakes are not only important for their aesthetic value but also for their ecological and cultural significance. Here is a detailed overview of the major lakes in Chamba District:
1. Khajjiar Lake

- Location: Khajjiar, also known as the “Mini Switzerland of India.”
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: Surrounded by dense cedar forests and a large meadow, Khajjiar Lake is renowned for its picturesque setting. The lake’s clear waters reflect the surrounding landscape, making it a popular tourist destination.
2. Manimahesh Lake

- Location: Located at the base of Mount Manimahesh in the Bharmour region.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: Known for its religious significance, Manimahesh Lake is considered sacred and is a significant site for Hindu pilgrims. The lake is surrounded by snow-capped peaks and is the focal point of the annual Manimahesh Yatra.
3. Chamera Lake

- Location: Near the Chamera Dam, in the Chamba District.
- Type: Artificial lake.
- Features: Created by the Chamera Dam on the Ravi River, this lake serves as a reservoir for hydroelectric power generation. It offers stunning views and is an important site for local water management and energy production.
4. Ghadassaru Lake
- Location: Near the village of Ghadassaru.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A lesser-known but picturesque lake surrounded by rugged terrain and dense forests. It is a peaceful spot ideal for those seeking solitude and natural beauty.
5. Lama Dal Lake
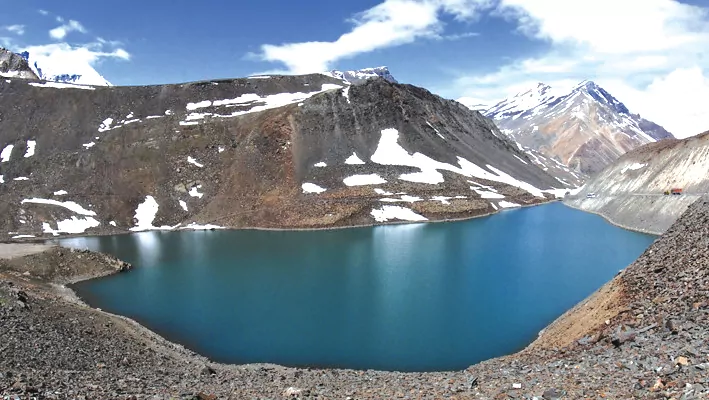

- Location: Situated in the Bharmour region.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A high-altitude lake known for its serene beauty and the surrounding alpine landscape. It is less frequented by tourists, providing a more secluded experience.
6. Mahakali Lake
- Location: In the remote areas of Chamba.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A tranquil lake that holds religious and cultural significance for the local communities. It is surrounded by pristine natural beauty.
7. Chandrakup Lake
- Location: In the northern parts of the district.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: Known for its clear waters and scenic surroundings. It is less visited but offers a unique view of the landscape.
8. Chamunda Lake
- Location: Near the Chamunda Devi Temple.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: This lake is located close to a major religious site and is often visited by pilgrims. It is known for its peaceful environment and spiritual significance.
9. Khajund Lake
- Location: In the vicinity of Khajund village.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A small yet beautiful lake that complements the natural landscape of the region.
10. Chakund Lake
- Location: Near Chakund village.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A tranquil lake offering a serene environment, ideal for nature lovers and those seeking a quiet retreat.
Lakes in the Dhauladhar Range
1. Nagara Lake
- Location: In the Dhauladhar Range.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: Known for its scenic beauty and high-altitude location. The lake is surrounded by snow-capped peaks and lush green meadows.
2. Kali Kund
- Location: In the Dhauladhar Range.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A pristine lake offering stunning views of the surrounding mountains and forests.
3. Dham Godi
- Location: In the Dhauladhar Range.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A small yet picturesque lake known for its clear waters and scenic surroundings.
4. Kali Dal
- Location: In the Dhauladhar Range.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: Known for its tranquil setting and the unique flora and fauna found around it.
5. Nag Dal
- Location: In the Dhauladhar Range.
- Type: Natural lake.
- Features: A high-altitude lake offering breathtaking views and a serene environment.
Conclusion
The lakes of Chamba District are integral to its natural landscape, providing not only aesthetic value but also contributing to the local ecosystem and cultural heritage. Whether it’s the sacred waters of Manimahesh Lake or the serene beauty of Khajjiar Lake, each lake has its unique charm and significance.
River System of Chamba District
The rivers in Chamba District are crucial to its ecological and geographical landscape:
- Ravi River: Originates from the glaciers of the Greater Himalayas, flows through Chamba District, and eventually merges into the Chenab River in Pakistan.
- Chenab or Chandrabhaga River: Formed by the confluence of the Chandra and Bhaga rivers, this river enters Chamba District’s Pangi Valley and flows into Kashmir.
Mountain Ranges in Chamba District
The district is surrounded by several prominent mountain ranges:
- Zanskar Range: Extends from the northeastern part of Himachal Pradesh, separating Ladakh from Lahaul and Spiti, and extends into Chamba.
- Dugani Dhar: A branch of the Pangi Range, it forms a boundary between Chamba and Bhaderwah in Jammu, including the Padri and Chattar Dhar passes.
- Pangi Range: Part of the main Himalayan axis, it divides Chamba into two distinct regions and separates it from Lahaul and Spiti.
- Hathidhar (Snowless Range): Lies parallel to the southern part of the Dhauladhar Range, forming part of the Shivalik range.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What was the total population of Chamba District according to the 2011 Census?
B) 519,080
2. Which lake in Chamba District is known as an artificial lake?
C) Chamera Lake
3. What is the name of the southern branch of the Pangi Range?
B) Manimahesh
4. With which river does the Ravi River merge?
A) Chenab River
5. Which mountain range in Chamba District is referred to as part of the inner Shivalik range?
C) Hathidhar
6. Which river is also known as Chandrabhaga in Chamba District?
D) Chenab River
7. Which lake is NOT included in the Dhauladhar Range?
C) Ghadassaru Lake
8. Which lake in Chamba District is considered to have religious significance?
B) Manimahesh Lake
9. What are the major tributaries of the Chenab River in Chamba District?
B) Miyar Nala and Sachu Nala
10. How many tehsils are there in Chamba District?
C) 7
For more information on the geography of Himachal Pradesh, you may find the following articles useful:
- Geography of Lahaul: Explore the unique geographical features of Lahaul.
- Geography of Mandi: Delve into the diverse landscape of Mandi District.
- River System in Mandi District: Understand the river systems that shape Mandi District.
- Lakes of Himachal Pradesh: Discover the serene lakes across Himachal Pradesh.
Geography and Climate of Chamba
Geography:
Location: Chamba is situated in Himachal Pradesh, India, and is the headquarters of the Chamba district. It is bordered by Jammu and Kashmir’s Kishtwar and Doda districts to the northwest, Ladakh and Lahaul and Bara Banghal to the northeast and east, Kangra to the southeast, and Punjab’s Pathankot district to the south. The town lies at an elevation of approximately 1,006 meters (3,301 feet) above sea level.
Rivers and Terrain: The town is located at the confluence of the Ravi River and its tributary, the Sal River. The Ravi River flows east-west, creating deep canyons. The town is set on flat terraces on the right bank of the Ravi River valley and is bounded by the Dhauladhar and Pir Panjal ranges.
Connectivity: Despite its hill location, Chamba is well connected by road to major cities like Shimla, Delhi, and Chandigarh. The nearest broad gauge railway stations are Chakki Bank and Pathankot, with Pathankot being 120 kilometers (75 miles) away by road.
Climate:
Temperature:
- Summer: Temperatures range from 38°C (100°F) to 15°C (59°F). The highest recorded summer temperature is 40.6°C (105.1°F).
- Winter: Temperatures range from 15°C (59°F) to 0°C (32°F). The lowest recorded winter temperature is -1°C (30°F).
Rainfall: The average annual rainfall is 785.84 millimeters (30.939 inches). Rainfall is concentrated between March and August, with July and August receiving the most precipitation.
Best Time to Visit: The period from March to June is considered the best time to visit Chamba due to favorable weather conditions.
Demographics
Population: As of the 2001 Census, Chamba had a population of 20,312. Males made up 52% of the population, and females 48%.
Literacy Rate: The average literacy rate in Chamba is 81%, higher than the national average of 59.5%. Male literacy is 85%, while female literacy is 77%.
Languages:
- Administrative Language: Hindi
- Locally Spoken Languages: Chambeali, with some speakers of Punjabi and Pashto.
Tribal Groups: The region has two major tribal groups:
- Gujjars: Nomadic herdsmen who travel to lowland Punjab in autumn.
- Gaddis: Primarily agricultural people, including Brahmans, Rajputs, Thakurs, Rathis, and Khatris.
Administration
Historical Rule: Chamba was ruled by a series of rajas, with a total of 67 rajas overseeing the area since the 6th century. The kingdom remained independent for over 1,000 years.
Administrative Divisions: Historically, Chamba was divided into five mandalas or wazarats: Chamba, Bharmour, Bhatti, Churah, and Pangi.
Landmarks and Cityscape
- Old Town vs. British Period Architecture:
- Old Town: Features traditional structures made from local materials, including temples and palaces. Key monuments include the Champavati Temple, Lakshmi Narayan temples, and the Chamunda Devi Temple.
- British Period: The British introduced new urban planning and architectural styles, including civic buildings around the Chaugan, suspension bridges, and other public welfare projects. Notable structures from this period include the Church of Scotland, Bhuri Singh Museum, and the Akhand Chandi Palace.
Culture
Arts: Chamba is renowned for its Pahari miniature paintings, which often feature Hindu religious themes. The art has evolved with influences from both Mughal and local styles.
Handicrafts: Traditional crafts include metalware, textiles such as Chamba shawls, traditional footwear, and wood carvings. The town also produces a variety of musical instruments.
Festivals and Fairs:
- Suhi Mata Mela: Celebrated annually to honor the sacrifice of a queen who brought water to the town.
- Minjar Mela: An important festival featuring various cultural and religious activities.
Wildlife Sanctuaries in Chamba District
Chamba District in Himachal Pradesh is home to several renowned wildlife sanctuaries, each offering unique habitats and ecosystems. These protected areas play a crucial role in conserving the diverse flora and fauna of the region. Here’s a detailed overview of the key wildlife sanctuaries in Chamba:
1. Gamgul Siyabehi Wildlife Sanctuary
The Gamgul Siyabehi Wildlife Sanctuary covers an area of 108.40 square kilometers and is located at a high altitude in Chamba District. The sanctuary is known for its rugged terrain and diverse wildlife. It serves as a crucial habitat for various species, including several that are native to the high-altitude regions of Himachal Pradesh.
2. Kalatop Khajjiar Wildlife Sanctuary
The Kalatop Khajjiar Wildlife Sanctuary is a significant protected area known for its lush landscapes and rich biodiversity. Nestled near the picturesque town of Khajjiar, this sanctuary is famous for its scenic beauty and the variety of wildlife it supports.
3. Kugti Wildlife Sanctuary
The Kugti Wildlife Sanctuary is the second largest sanctuary in Himachal Pradesh, covering a vast area. It is renowned for its diverse wildlife and the presence of the Manimahesh Temple, a site of immense religious significance that attracts thousands of pilgrims annually. This sanctuary is a vital area for the protection of wildlife and natural habitats in the region.
4. Sechu Tuan Nala Wildlife Sanctuary
Spanning 390.20 square kilometers, the Sechu Tuan Nala Wildlife Sanctuary is located approximately 113 kilometers from Chamba town. This extensive sanctuary plays a crucial role in the conservation of the local ecosystem and provides a sanctuary for various wildlife species in Chamba District.
5. Tundah Wildlife Sanctuary
The Tundah Wildlife Sanctuary covers an area of 64 square kilometers and was established to protect the wildlife and their habitats in Chamba District. Situated 59 kilometers from Chamba town, this sanctuary is an important area for the conservation of several species and the preservation of their natural environment.
These sanctuaries not only help in preserving the rich biodiversity of Chamba but also contribute to the ecological balance and conservation efforts in Himachal Pradesh.
Geography and Climate
What is the average elevation of Chamba? A) 800 meters
B) 1,006 meters
C) 1,200 meters
D) 1,500 meters
Answer: B) 1,006 metersWhich river flows through Chamba? A) Chenab River
B) Ravi River
C) Jhelum River
D) Beas River
Answer: B) Ravi RiverWhat is the highest recorded temperature in Chamba during summer? A) 38.5 °C
B) 40.6 °C
C) 42.3 °C
D) 45.0 °C
Answer: B) 40.6 °CWhich of the following is the best period to visit Chamba according to its climate data? A) January to February
B) July to August
C) March to June
D) September to November
Answer: C) March to JuneWhat is the average annual rainfall in Chamba? A) 785.84 mm
B) 1,190.9 mm
C) 1,500 mm
D) 2,000 mm
Answer: A) 785.84 mm
Demographics
According to the 2001 census, what was the population of Chamba? A) 15,000
B) 20,312
C) 25,000
D) 30,000
Answer: B) 20,312What is the average literacy rate of Chamba? A) 70.8%
B) 75.3%
C) 80.1%
D) 85.7%
Answer: A) 70.8%What was the population density of Chamba according to the 2001 census? A) 2,500 people per square kilometer
B) 3,000 people per square kilometer
C) 3,500 people per square kilometer
D) 4,000 people per square kilometer
Answer: B) 3,000 people per square kilometer
Historical and Cultural Aspects
When was Chamba established as a municipality? A) 1880
B) 1890
C) 1900
D) 1910
Answer: A) 1880Which festival is prominently celebrated in Chamba? A) Diwali
B) Lohri
C) Baisakhi
D) Holi
Answer: C) BaisakhiWhich historical monument is located in Chamba? A) St. Mary’s Church
B) Bhuri Singh Museum
C) Qutb Minar
D) Red Fort
Answer: B) Bhuri Singh MuseumWhich of the following is a traditional craft of Chamba? A) Wood Carving
B) Pottery
C) Weaving
D) Metalwork
Answer: A) Wood Carving
Economy and Infrastructure
What is a major economic activity in Chamba? A) Mining
B) Agriculture
C) IT services
D) Manufacturing
Answer: B) AgricultureWhich type of transportation is primarily used in Chamba? A) Railways
B) Airways
C) Roadways
D) Waterways
Answer: C) RoadwaysWhat is the major source of water for Chamba? A) Rivers
B) Lakes
C) Wells
D) Rainwater harvesting
Answer: A) Rivers
Education and Health
What is the name of a notable educational institution in Chamba? A) Government Degree College
B) Chamba School of Engineering
C) Chamba Medical College
D) Central University of Chamba
Answer: A) Government Degree CollegeWhat healthcare facility is significant in Chamba? A) Chamba General Hospital
B) City Health Center
C) District Medical Office
D) Private Clinic
Answer: A) Chamba General Hospital
Environmental Issues
Which of the following is a significant environmental concern in Chamba? A) Air pollution
B) Water scarcity
C) Deforestation
D) Soil erosion
Answer: C) DeforestationWhat kind of vegetation is commonly found in Chamba? A) Desert flora
B) Tropical rainforests
C) Alpine forests
D) Grasslands
Answer: C) Alpine forestsWhat is a major challenge for agriculture in Chamba? A) High soil salinity
B) Extreme temperatures
C) Lack of irrigation facilities
D) Frequent floods
Answer: C) Lack of irrigation facilities