Table of Contents
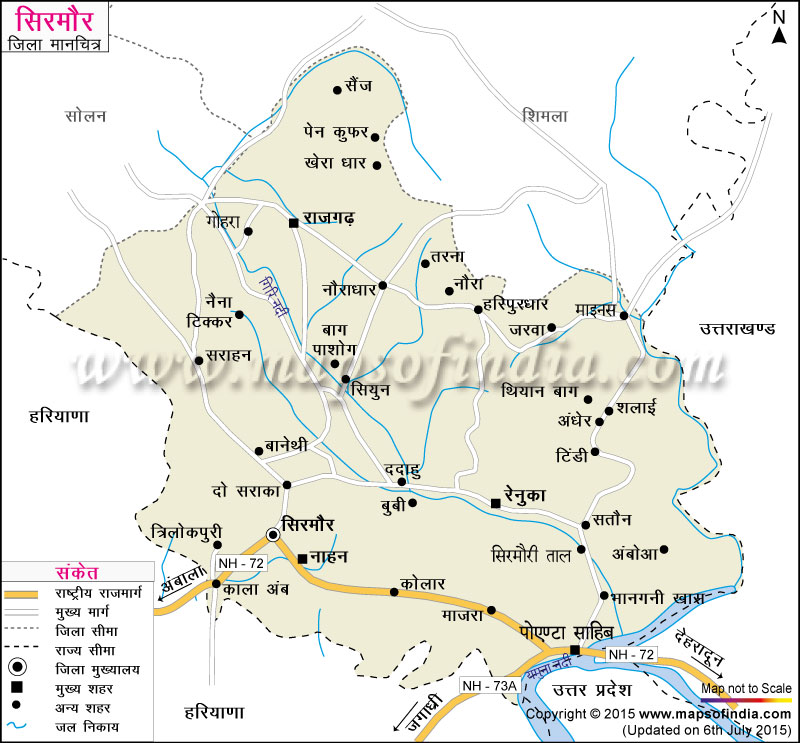
Brief Geography of Sirmaur District
Geographical Location:
- Location: Sirmaur District is situated in the southern part of Himachal Pradesh.
- Boundaries: It is bordered by Shimla to the north, Yamunanagar (Haryana) to the west, Kinnaur to the east, and Solan to the northeast.
- Altitude: Ranges from 450 meters to 2,500 meters above sea level.
Natural Geography:
- Topography: The district is predominantly hilly and rugged, located in the lower Himalayan region of the Shivalik Hills.
- Rivers: Major rivers include the Yamuna and its tributaries like Tons, Giri, and Ponda. The Yamuna River forms the southern boundary of Sirmaur District.
- Mountain Ranges: The main mountain range in Sirmaur is the Shivalik range, which significantly influences the district’s geography.
- Plains: There are narrow plains in some areas, primarily around river valleys.
Main Mountain Ranges:
- Shivalik Range: This range covers most of the district and is the primary mountain range here.
- Auxiliary Hills: Notable hills in these ranges include Sangla, Kunjhar, and Churuwal.
Climate:
- Seasonal Effects: The climate varies significantly. Summers can be quite hot, while winters are cold. Heavy rainfall occurs during the monsoon season.
- Rainfall: Annual average rainfall ranges from 800 mm to 1,500 mm.
Flora and Forests:
- Vegetation: The natural vegetation includes trees like Shimla pine, deodar, and oak.
- Forests: The district features various types of forest areas, including dense forests and mixed coniferous forests.
Size and Location of Sirmaur District:
- Location: Situated in the southeastern part of Himachal Pradesh, it includes the region known as the Kyar-da-Doon valley.
- Borders:
- North: Shimla District
- Northwest: Solan District
- West and South: Haryana State
- East: Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh States
- Area:
- Total Area: 2,825 square kilometers
- Ranking: 7th largest district in the state by area.
- Villages:
- Total Villages: 976
- Habitable Villages: 968
Also Read This: Census Of Sirmaur District 2011
Sub-Regions:
- Upper Sirmaur Forest Area
- Siss-Giri Region
- Sirmaur Shivalik
- Kyar-Doon Valley
Special Locations:
- Churdhar: A prominent peak forming a boundary between Shimla and Sirmaur districts, crucial for the region’s geographical identity.
- Haripur Dhar: Previously known as ‘Dungbhangyani,’ it was the summer capital of Sirmaur and has a fort built to defend against neighboring Jubbal.
River and Lake Systems:
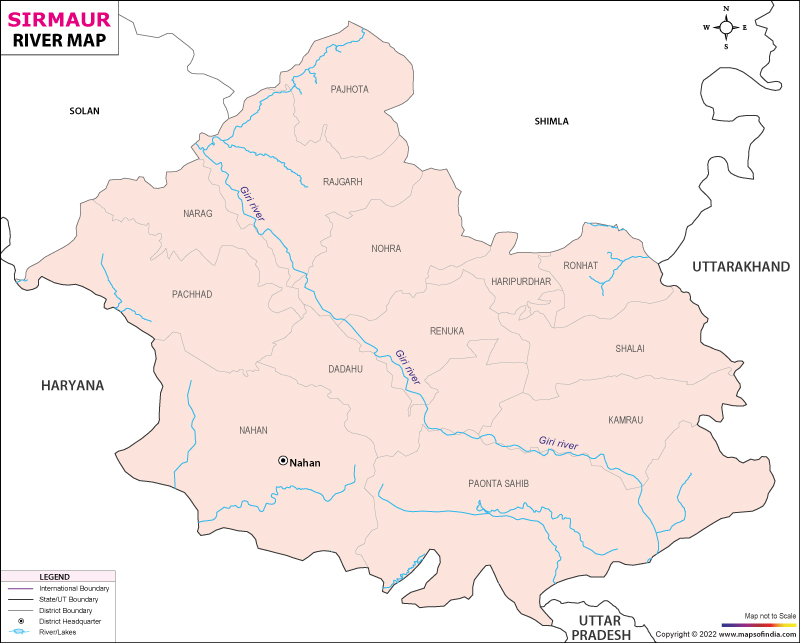
Major Rivers:
- Yamuna River: Originates from Yamunotri Glacier in Uttarakhand. Enters Sirmaur at Khadar Majri and exits at Tajewala. It forms the southern boundary of the Kyar-da-Doon.
- Giri River: Originates from Kuppar Peak in Shimla District. Enters Sirmaur at Mariog village and flows southeast, dividing Sirmaur into two equal parts. Joins Yamuna River at Rampura Ghat.
- Tons River: Originates from Yamunotri Mountain. Enters Sirmaur near Kot/Koti village and forms the eastern boundary of the district.
- Markanda River: Originates from the Katasan Pass and exits Sirmaur at Kala Amb into Haryana.
- Bata River: Originates from Siori Falls in the Dharti Mountain Range and divides the Kyar-da-Doon. Joins Yamuna River at Mandi.
- Neera River: Forms a boundary between Kamru and Shillai tehsils.
- Ghaggar River: Originates near Luvasa in Sirmaur and exits at Preet Nagar into Haryana.
Rivers and Lakes
Yamuna River
- Source: The Yamuna River originates from the Yamunotri glacier in the Himalayas at an altitude of approximately 7,924 meters above sea level.
- Course: Flowing through the Garhwal region and the Jaunsar area, it covers about 22 kilometers before entering the eastern boundary of Sirmaur district. It separates the Kyar-Da-Doon region from Dehradun, marking the boundary between Sirmaur and Uttarakhand.
- Characteristics: Within Sirmaur, the river’s estimated maximum width is 90 meters and depth is 6 meters, though this can increase significantly during the monsoon season. In summer, the water volume fluctuates due to snowmelt from the mountains. The river’s water is generally cold and clear but can become muddy during the summer. The Yamuna is a sacred river with temples and a gurdwara along its banks. The river’s lower elevations make it unsuitable for irrigation in the Kyar-Da-Doon plateau. Historically, timber was floated down the river, but now it is transported by motor vehicles.
- Tributaries: The notable tributaries include the Tons, Giri, and Bata rivers, which join the Yamuna at different points such as Khodri Majri, Rampur Ghat, and Bata Mandi.
Giri River
- Course: The Giri River drains a significant portion of the district and originates from the hills of Jubbal and nearby areas in Shimla district. It flows southwest, forming a boundary with Shimla district for about 40 kilometers. It meets the Yamuna at Rampur Ghat.
- Characteristics: The Giri River supports a canal system, and boating is available at Shyampur. It is known for the Mahseer fish. Timber is transported from the river to the Yamuna, and irrigation is practiced at some locations.
- Tributaries: Important tributaries include the Nait and Palor on the left bank, and the Bagthi, Pravi, Khal, and Joggar on the right bank.
Tons River
- Source: The Tons River also originates in the Yamunotri region and flows through the regions of Jubbal and Jaunsar before joining the Yamuna at Khodri Majri. It flows at an elevation of approximately 3,897 meters, creating a grand confluence with the Yamuna.
- Characteristics: The Tons River has a scenic, rapid flow as it cascades over rocks, showcasing its significance and natural beauty.
Jalal River
- Course: This small, shallow river originates in the Pachhad tehsil near Bani village and flows between the Sanidhar and Dharti Dhar ridges. It merges with the Giri River near Dadahu.
- Characteristics: The river is easily crossable but can become quite tumultuous during the monsoon, presenting a dramatic sight.
Markanda River
- Source: The Markanda River originates in the hilly areas of Badaban near Katasan and flows through the region below the Katasan Devi temple.
- Course: It flows southeast and southwest for about 24 kilometers in Sirmaur district, irrigating the Bajora area before entering Ambala district at Kala Amb. It widens significantly at the village of Devni.
- Characteristics: The river is connected to the Salani River and irrigates various areas, providing water to some factories as well.
Bata River
- Source: The Bata River originates in the Bagna village of the Sioli area in the Nahan tehsil and flows eastward, dividing the Kyar-Da-Doon region.
- Course: It irrigates a large area of the Doon before joining the Yamuna at Bata Mandi. During the monsoon, the river can become extremely voluminous and turbulent.
Lakes:
- Renuka Lake: Located near Dadahu in Sirmaur, it is the only lake in the district and is associated with the legend of the goddess Renuka.
Water Sources: Drinking water in the district comes from natural springs, Shivpuri Spring, and Nahar Sabar Springs.
जिला सिरमौर का संक्षिप्त भूगोल
भौगोलिक स्थिति:
- स्थान: जिला सिरमौर हिमाचल प्रदेश के दक्षिणी भाग में स्थित है।
- सदस्यताएँ: उत्तर में शिमला, पश्चिम में यमुनानगर (हरियाणा), पूर्व में किन्नौर और उत्तर-पूर्व में सोलन जिलों से घिरा हुआ है।
- समुद्र तल से ऊंचाई: 450 मीटर से 2,500 मीटर के बीच।
प्राकृतिक भूगोल:
- भू-आकृति: सिरमौर जिला मुख्यतः पहाड़ी और उबड़-खाबड़ है। यह क्षेत्र शिवालिक श्रेणी के निचले हिमालयी क्षेत्र में स्थित है।
- नदियाँ: प्रमुख नदियाँ यमुना और उसकी सहायक नदियाँ जैसे कि टौंस, गिरी, और पोंडो है। यमुना नदी जिला सिरमौर की दक्षिणी सीमा बनाती है।
- पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ: सिरमौर में मुख्यतः शिवालिक श्रृंखला है जो जिले की भौगोलिक पहचान को प्रमुख रूप से प्रभावित करती है।
- समतल क्षेत्र: कुछ हिस्सों में संकीर्ण समतल क्षेत्र हैं, जो नदी घाटियों के आसपास स्थित हैं।
मुख्य पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ:
- शिवालिक पर्वत श्रृंखला: यह पर्वत श्रृंखला जिले के अधिकांश हिस्से को कवर करती है और यहां की प्रमुख पर्वत श्रृंखला है।
- सहायक पहाड़ियाँ: इन पर्वत श्रृंखलाओं में कुछ प्रमुख पहाड़ियाँ जैसे कि संगला, कुंजर और चुरुवाल शामिल हैं।
जलवायु:
- मौसमी प्रभाव: जिला सिरमौर में मौसमी परिवर्तन काफी भिन्न होते हैं। गर्मी के मौसम में तापमान उच्च हो सकता है जबकि सर्दी के मौसम में ठंडक बनी रहती है। मानसून के दौरान भारी वर्षा होती है।
- वर्षा: सालाना औसत वर्षा 800 मिमी से 1,500 मिमी के बीच होती है।
वनस्पति और वन:
- वनस्पति: जिले में प्राकृतिक वनस्पति में मुख्यतः शिमला पाइन, देवदार, और ओक जैसे पेड़ शामिल हैं।
- वन: सिरमौर जिले में विभिन्न प्रकार के वन क्षेत्र हैं, जिनमें घने वन और बांज-चिल के वन शामिल हैं।
जिला सिरमौर का आकार और स्थान
भौगोलिक स्थिति:
- स्थान: जिला सिरमौर हिमाचल प्रदेश के दक्षिण-पूर्वी भाग में स्थित है, जो बाहरी हिमालय (शिवालिक) के क्षेत्र में आता है। इसे कयार-दा-दून के नाम से जाना जाने वाला दून घाटी का क्षेत्र भी शामिल है।
- संगठन: सिरमौर जिला हिमाचल प्रदेश हिमालय क्षेत्र के दक्षिणी हिमाचल प्रदेश का एक हिस्सा है।
- सीमाएं:
- उत्तर: शिमला जिला
- उत्तर-पश्चिम: सोलन जिला
- पश्चिम और दक्षिण: हरियाणा राज्य
- पूर्व: उत्तराखंड और उत्तर प्रदेश राज्य
- क्षेत्रफल:
- कुल क्षेत्रफल: 2,825 वर्ग किमी
- राज्य में स्थान: क्षेत्रफल की दृष्टि से राज्य के जिलों में सिरमौर का 7वां स्थान है।
- गांव:
- कुल गांव: 976
- रहने योग्य गांव: 968
उप-सूक्ष्म क्षेत्र: जिला सिरमौर को चार उप-सूक्ष्म क्षेत्रों में विभाजित किया गया है:
- ऊपरी सिरमौर वन क्षेत्र
- सीस-गिरि क्षेत्र
- सिरमौर शिवालिक
- क्यारदून घाटी
विशेष स्थल:
- चूड़धार: शिमला और सिरमौर जिलों के बीच सीमा बनाता है, जो इस क्षेत्र की भौगोलिक पहचान में महत्वपूर्ण है।
जिला सिरमौर का भूगोल: ट्रांस-गिरि और सीस-गिरि क्षेत्र
ट्रांस-गिरि क्षेत्र:
- चूड़धार:
- प्रमुख चोटी: चूड़धार, जिसे चूड़ चांदनी की धार भी कहते हैं, जिले की एक प्रसिद्ध चोटी है।
- अन्य प्रमुख धारें:
- टपरोली-जडोल धार
- नोहरा धार
- हरिपुर धार
- धूधम धार
- कमरौ धार
- धार निगाली
- धार शिलाई
ये धारें इस क्षेत्र की प्रमुख पर्वतीय श्रृंखलाएं हैं और भूगोलिक दृष्टि से महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
सीस-गिरि क्षेत्र:
- गिरि नदी:
- यह क्षेत्र को ट्रांस-गिरि क्षेत्र से विभाजित करती है।
- मारकंडा नदी:
- इस क्षेत्र के पश्चिमी भाग में बहती है।
- कायार-दा-दून:
- इस क्षेत्र की समतल घाटी को कायार-दा-दून के नाम से जाना जाता है, जो “बाटा” नदी द्वारा सिंचित होती है।
- सियान धार और धरती धार:
- सियान धार और धरती धार इस क्षेत्र की प्रमुख धारें हैं।
- जलाल नदी: सियान धार और धरती धार को विभाजित करती है।
- सैन धार:
- यह उत्तर-पश्चिम से दक्षिण-पूर्व दिशा में गिरि नदी के समानांतर फैली हुई है और ददाहू में गिरि नदी के बाएं तट पर समाप्त होती है।
- धरतीधार:
- यह सैनधार के समानांतर चलती है और दक्षिण-पूर्व की ओर इस क्षेत्र की सीमा के साथ-साथ आगे बढ़ती है।
- भू-आकृति: इस क्षेत्र का उत्तर-पूर्वी भाग अपेक्षाकृत अधिक ऊंचाई पर स्थित है।
जैतक पहाड़ियाँ:
- इतिहास: जैतक पहाड़ियों पर गोरखाओं द्वारा 20 किलों का निर्माण किया गया था और सबसे महत्वपूर्ण लड़ाई 1814-15 में गोरखाओं और अंग्रेजों के बीच लड़ी गई थी।
हरिपुर धार:
- पुराना नाम: पहले इसे ‘डुंगभंगयाणी’ के नाम से जाना जाता था।
- इतिहास: पहले यह सिरमौर की ग्रीष्मकालीन राजधानी थी।
- किला:
- इस पर्वतमाला पर एक किला मुख्य रूप से पड़ोसी राज्य जुब्बल के साथ राज्य की सीमाओं की रक्षा के लिए बनाया गया था।
जिला सिरमौर का नदी और झील प्रणाली
प्रमुख नदियाँ
- यमुना नदी:
- उत्पत्ति: उत्तराखंड में यमुनोत्री ग्लेशियर से।
- सिरमौर में प्रवेश: खादर माजरी में।
- जिले से बाहर निकलना: ताजेवाला में।
- भौगोलिक भूमिका: यह क्यार-दा-दून को देहरादून से अलग करती है और सिरमौर तथा उत्तराखंड के बीच सीमा बनाती है।
- मुख्य सहायक नदियाँ: टोंस, गिरि, और बाटा।
- गिरि नदी:
- उत्पत्ति: शिमला जिले की जुब्बल तहसील में कुपार चोटी से।
- सिरमौर में प्रवेश: उत्तर दिशा से मरिओग गांव में।
- प्रवाह: पूर्व-दक्षिण दिशा में मंडुपलासा गांव से गुजरते हुए सिरमौर को दो बराबर भागों में विभाजित करती है।
- विलय स्थान: रामपुरा घाट पर यमुना नदी में।
- मुख्य सहायक नदियाँ: जलाल, नैत, पलोर, बसारी और कवल।
- बायां किनारा सहायक नाले: पेरवी, नैट, पलोर और जगत नाले।
- दायां किनारा सहायक नाला: कमली नाला।
- जलाल नदी:
- सहायक नदी: गिरि नदी की महत्वपूर्ण सहायक नदी।
- मिलन स्थान: ददाहू में गिरि नदी के दाहिने किनारे पर।
- टोंस नदी:
- उत्पत्ति: यमुनोत्री पर्वत से।
- सिरमौर में प्रवेश: कोट/कोटी गाँव के पास।
- भौगोलिक भूमिका: उत्तराखंड के जौनसार क्षेत्र से अलग करती है।
- मुख्य सहायक नदियाँ: बाघल, नेवाली (या नैरा), और सैंज नदी।
- पूर्वी सीमा: सिरमौर की पूर्वी सीमा बनाती है।
- मारकंडा नदी:
- उत्पत्ति: कटासन दर्रे की पहाड़ी में बराबन से।
- प्रवाह: कटासन देवी के मंदिर के नीचे से।
- सिरमौर से बाहर निकलना: काला अंब में हरियाणा में प्रवेश करती है।
- बाटा नदी:
- उत्पत्ति: धरती पर्वतमाला में सिओरी झरने से।
- भौगोलिक भूमिका: कयार-दा-दून को दो बराबर भागों में विभाजित करती है।
- विलय स्थान: मंडी में यमुना नदी में।
- नेरा नदी:
- भौगोलिक भूमिका: कमरऊ उप-तहसील और शिलाई तहसील की सीमा बनाती है।
- घग्गर नदी:
- उत्पत्ति: सिरमौर जिले में लवासा के पास।
- सिरमौर से बाहर निकलना: प्रीत नगर में हरियाणा में प्रवेश करती है।
झीलें
- रेणुका झील:
- स्थान: सिरमौर जिले में, ददाहू के नजदीक।
- विशेषता: यह जिले की एकमात्र झील है और परशु राम की मां रेणुका देवी से जुड़ी है।
- जल स्रोत: जिले में पीने का पानी प्राकृतिक झरनों, शिवपुरी झरने, और नहर साबर झरनों से प्राप्त होता है।
Demographics and Geography of Sirmaur District
Population (According to Census 2011):
- Total Population: 529,855
- Male Population: 276,289
- Female Population: 253,566
- Sex Ratio: 918 females per 1,000 males
- Density of Population: 188 people per square kilometer
Geographical Area:
- Total Geographical Area: 224,759 hectares
- Area under Forest: 48,682 hectares
- Total Cultivated Area: 75,914 hectares
- Cultivated Area: 40,235 hectares
- Net Irrigated Area: 15,196 hectares
- Area Sown More Than Once: 35,679 hectares
- Altitude: 3,647 meters
- Longitude: 77° 01’12” to 77°49’40” East
- Latitude: 30°22’30” to 31°01’20” North
Major Rivers:
- Yamuna
- Giri
- Tons
- Jalal
Culture:
- Major Religions: Hinduism, Sikhism, Islam
- Languages Spoken: Hindi, Phari, Punjabi
Literacy Rates:
- Total Literacy Rate: 78.8%
- Male Literacy Rate: 85.6%
- Female Literacy Rate: 71.4%
National Parks & WildLife Sanctuary
Simbalbara National Park
Overview:
- Designation: Declared a national park in 2010
- Location: Sirmaur District, Himachal Pradesh
- Area: Approximately 27.88 square kilometers
Flora:
- Vegetation: The park features Sal forests and lush green pastures.
Fauna:
- Mammals:
- Goral
- Spotted Deer
- Sambhar
- Himalayan Black Bear
- Hanuman Langurs
- Indian Muntjacs
Simbalbara National Park is known for its diverse wildlife and rich vegetation, making it an important ecological area in the region.
Renuka Wildlife Sanctuary

Location and Area:
- Location: Near Renuka Lake, Sirmaur District, Himachal Pradesh
- Core Area: 402 hectares
- Buffer Belt: Additional 300 hectares outside the core area
Flora:
- Forest Type: Mixed deciduous forest
- Dominant Trees: Sal, Shisham, Khair
- Vegetation: Includes various climbers in moist depressions
Fauna:
- Mammals:
- Leopard
- Sambhar
- Spotted Deer
- Barking Deer
- Jackal
- Black Bear
- Porcupine
- Birds:
- Red Jungle Fowl
- Khaleej Pheasant
- Blue Jay
- Black Partridge
- Drongos
- Scarlet Minivet
- Common Coots
Additional Features:
- Mini Zoo: Houses rescued, stray, and deserted animals from the forests
- Proximity: About 40 km from Nahan (district headquarters)
- Nearby Settlement: Dadahu (accessible by taxi or public transport)
Churdhar Sanctuary
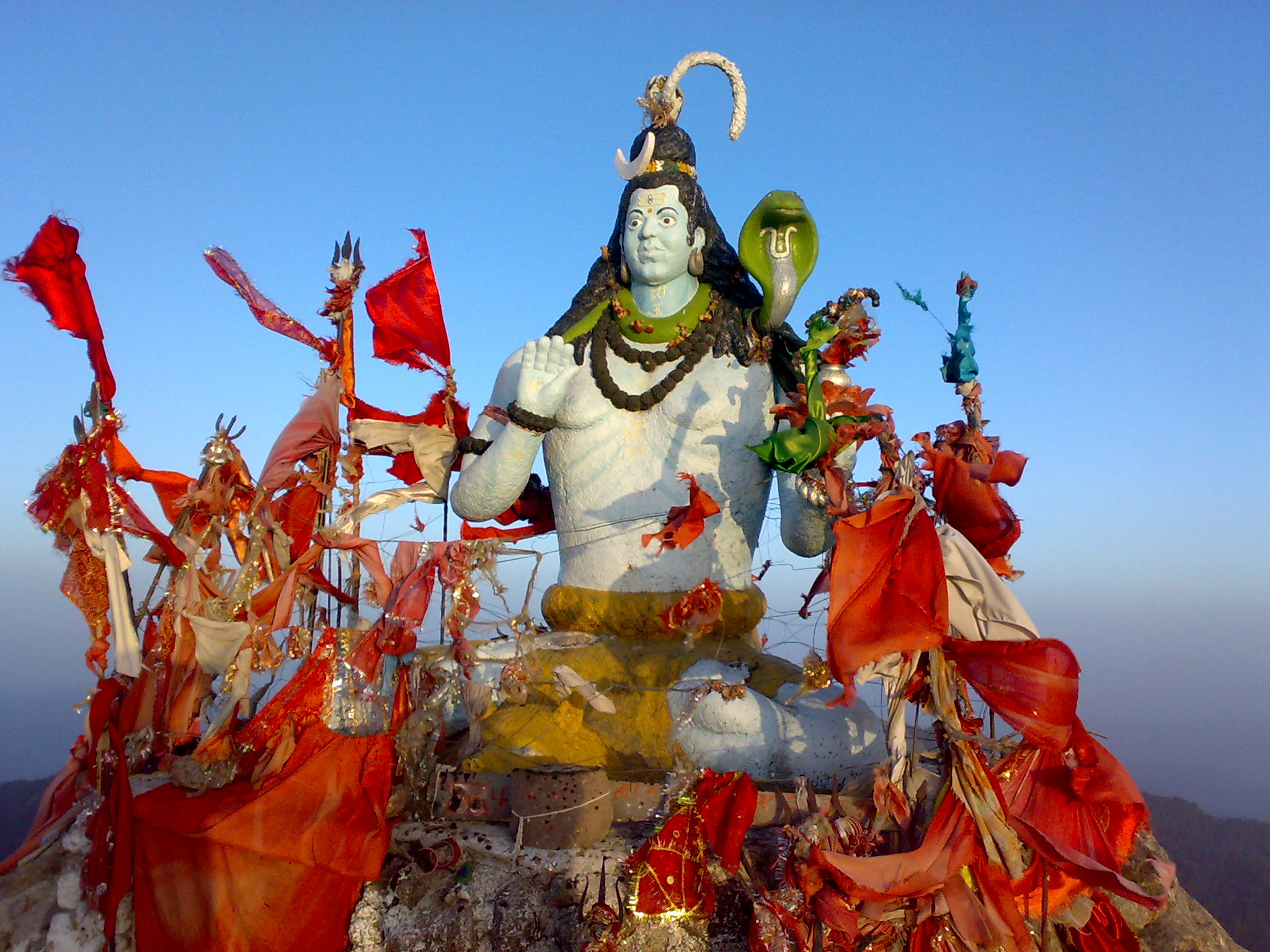

Location and Area:
- Location: Along the Churdhar Range, Sirmaur District
- Area: 56.16 square kilometers
Flora:
- Forest Type: Western mixed coniferous forest
- Dominant Trees: Cedar, Blue Pine, Spruce, and large plantations of Kharu Oaks
Fauna:
- Mammals:
- Leopard
- Himalayan Black Bear
- Barking Deer
- Ghoral
- Musk Deer
- Birds:
- Monal Pheasant
- Khaleej Pheasant
- Red Jungle Fowl
Access and Activities:
- Access: Reachable from Nohradhar in Sirmaur and Chopal in Shimla
- Activities: Several fine trekking trails are available in the sanctuary
Both sanctuaries are important for conservation and provide opportunities for wildlife observation and trekking.
Renuka Wildlife Sanctuary
Flora & Fauna:
- Bio-Geographical Zone: The sanctuary falls in bio-geographical zone IV and bio-geographical province IV as classified by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII).
- Forest Types:
- Dry mixed deciduous forest (Group 5B/C2)
- Dry Sal forest (Group 5/051)
- Flora:
- Trees: Anogeissus, Lucinea, Terminalia, Khair, Shisham, Carrie, Cordia
- Climbers: Various climbers in moist depressions
- Fauna:
- Mammals: Leopard, Sambhar, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer, Jackal, Hare, Jungle Cat, Palm Civet, Porcupine
- Birds: Blue Jay, Black Partridge, Drongos, Hill Crow, Scarlet Minivet, Bulbul, Common Coots, Green Pigeons
Mini Zoo & Lion Safari:

- History:
- Established: Renukaji Mini Zoo, the oldest zoo in Himachal Pradesh, was initiated in 1957.
- First Animal: A male spotted deer named Moti was the first animal.
- Early Additions: Female chital were brought to accompany Moti, and other animals like Sambhar, Chinkara, Hog Deer, and Black Buck were later introduced.
- Open Park: An open park was established in 1983 to accommodate the growing number of animals. Black Buck and Nilgai were brought from Pipli Zoo.
- Notable Additions:
- 1985: A pair of Mithun from Arunachal Pradesh.
- 1986: Another Mithun from Nagaland.
- 1975: A pair of Lions named Raja and Rani from Zunagarh.
- 1998-99: An aviary was added.
- Management:
- Sanctuary Management: The sanctuary is managed as the Renukaji Wildlife Range under the Shimla Wildlife Division.
- Staff: Increased staff to manage the sanctuary includes two beat guards, one Range Officer, and one Deputy Ranger.
- Fencing: The sanctuary’s perimeter is fenced to prevent illegal entry.
Staying Facilities:
- Hotel: The best accommodation near the lake is the Hotel ‘Renuka,’ run by the tourism department.
- Forest Department: An inspection hut of the forest department is available.
- Rest House: A rest house run by the State Electricity Board is located about 2 km away from Renuka Lake at Dadahu.
Lion Safari:
- Feature: The Lion Safari is a notable attraction in the sanctuary.
Renuka Wildlife Sanctuary is a significant conservation area with a variety of wildlife and plant species, along with facilities for visitors to enjoy and explore the natural beauty of the region.
Places of Interest
- Nahan
- Churdhar
- Jaitak Fort
- Haripurdhar
- Paonta Sahib
- Rajgarh
- Renuka Ji
- Sarahan
Nahan
English: Nahan, the district headquarters of Sirmaur, was established in 1621 by Raja Karm Prakash. Situated at an altitude of 932 meters, the city enjoys a pleasant climate year-round. Key attractions include the historic Mahal (Palace), and picturesque walking paths like Villa Round, Army Round, and Hospital Round, offering stunning views of the surrounding areas. The Rani Tal Garden, located right beneath the palace, is one of the most beautiful spots in the city. Nahan is also known for its well-equipped rest houses and other accommodation facilities.
Hindi: नाहन, सिरमौर जिले का मुख्यालय, 1621 में राजा कर्म प्रकाश द्वारा स्थापित किया गया था। समुद्र तल से 932 मीटर की ऊंचाई पर स्थित, यह शहर पूरे साल सुखद मौसम का आनंद लेता है। प्रमुख आकर्षणों में ऐतिहासिक महल और विला राउंड, आर्मी राउंड, और अस्पताल राउंड जैसे सुंदर पैदल पथ शामिल हैं, जो आसपास के क्षेत्रों के शानदार दृश्य प्रस्तुत करते हैं। महल के ठीक नीचे स्थित रानी ताल बाग शहर के सबसे सुंदर स्थानों में से एक है। नाहन अपने आधुनिक विश्राम गृहों और अन्य आवास सुविधाओं के लिए भी जाना जाता है।
Churdhar
English: Churdhar, standing at 11,982 feet, is the highest peak in the Shivalik range of Sirmaur district. Known as Chud-Chandani (Snow Crest), it offers breathtaking views of the southern foothills, snow-covered valleys, and the northern peaks of Badrinath and Kedarnath. The area is rich in medicinal herbs and alpine flora. The Shirgul Temple dedicated to Chudeshwar Mahadev Shiva is a significant pilgrimage site. Trekkers often traverse small glaciers and experience heavy snowfall. On a clear day, views of the Ganges plains and the hills of Shimla and Chakrota are visible.
Hindi: चूडधार, 11,982 फीट ऊँचा, सिरमौर जिले की शिवालिक पर्वतमाला का सबसे ऊँचा शिखर है। इसे चूड-चांदनी (बर्फ की चूड़ी) के रूप में जाना जाता है, जो दक्षिणी तलहटी, बर्फ से ढके उपत्यकाओं और बद्रीनाथ और केदारनाथ की उत्तरी चोटियों का अद्भुत दृश्य प्रदान करता है। यहाँ जड़ी-बूटियों और सुंदर अल्पाइन वनस्पतियों का भंडार है। शिरगुल मंदिर, जो चूडेश्वर महादेव शिव को समर्पित है, एक महत्वपूर्ण तीर्थ स्थल है। ट्रेकर्स अक्सर छोटे ग्लेशियरों से गुजरते हैं और भारी बर्फबारी का अनुभव करते हैं। एक साफ दिन पर गंगा के मैदान और शिमला और चकरोता की पहाड़ियों के दृश्य भी देखे जा सकते हैं।
Jaitak Fort
English: Jaitak Fort is historically significant in Sirmaur’s history. Located about 19 km north of Nahan on the Jamta-Nahan-Dadahu motorable road, the fort was built after the defeat of the Gorkhas in 1810. The fort offers scenic views of the Sain Dhar, Nahan, and Dharati Dhar hills. The village of Jaitak is a remnant of the once-important Jaitak dynasty.
Hindi: जैतक किला सिरमौर के इतिहास में महत्वपूर्ण स्थान रखता है। नाहन से लगभग 19 किमी उत्तर में जमटा-नाहन-दादाहू मोटर मार्ग पर स्थित, यह किला 1810 में गोरखाओं की हार के बाद बनाया गया था। किला सैंण धार, नाहन, और धरटी धार की पहाड़ियों के मनमोहक दृश्य प्रदान करता है। जैतक गाँव पूर्व-प्रमुख जैतक वंश का एक अवशेष है।
Haripurdhar
English: Haripurdhar is named after the hill near the Haripur region. The fort on the hill was built by the former rulers of Sirmaur to guard against encroachments from the neighboring Jubbal state. Although now largely obsolete, it was historically used to prevent external invasions. The fort area is ideal for hunting in the surrounding forests. The nearest access is via Rajgarh from Solan.
Hindi: हरीपुरधार हरीपुर नामक स्थान के निकट की पहाड़ी के नाम पर रखा गया है। पहाड़ी पर स्थित किला सिरमौर के पूर्ववर्ती शासकों द्वारा पड़ोसी जुब्बल राज्य के आक्रमणों से रक्षा के लिए बनाया गया था। हालांकि अब यह बड़े पैमाने पर अनुपयोगी हो गया है, इसका ऐतिहासिक उपयोग बाहरी आक्रमणों को रोकने के लिए किया गया था। किले के आस-पास के जंगल में आखेट करने के लिए यह जगह आदर्श है। निकटतम पहुंच सोलन से राजगढ़ के माध्यम से होती है।
Paonta Sahib

English: Paonta Sahib, located about 45 km from Nahan, is an important town in the Sirmaur district. It is known for the Paonta Sahib Gurudwara, where Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh Guru, resided from 1742 to 1745. The town is situated on the banks of the Yamuna River and is a sacred site for both Sikhs and Hindus. The name Paonta Sahib is derived from the legend that Guru Gobind Singh’s ornament, known as “Panta,” was lost in the river.
Hindi: पॉँवटा साहिब, नाहन से लगभग 45 किमी दूर, सिरमौर जिले का एक महत्वपूर्ण शहर है। यह प्रसिद्ध पॉँवटा साहिब गुरुद्वारे के लिए जाना जाता है, जहाँ गुरु गोविंद सिंह, सिखों के दसवें गुरु, 1742 से 1745 तक रहे थे। यह शहर यमुना नदी के किनारे स्थित है और सिखों और हिंदुओं दोनों के लिए एक पवित्र स्थल है। पॉँवटा साहिब का नाम एक किंवदंती से आया है कि गुरु गोविंद सिंह का आभूषण “पाँटा” नदी में खो गया था।
Rajgarh
English: Rajgarh, the largest sub-division of Sirmaur district, is known for its lush green valley. With a population of 76,509, it includes the sub-divisions of Rajgarh and Sarahan. The area is famous for its production of peaches and other stone fruits. The local people, primarily from the Khsh Rajput clan, played a significant role in the freedom struggle. The valley’s people are known for their progressive nature and devotion to deities like Shiva and Devi Durga.
Hindi: राजगढ़, सिरमौर जिले का सबसे बड़ा उप-मंडल, हरी-भरी घाटी के लिए जाना जाता है। 76,509 की आबादी वाला यह क्षेत्र राजगढ़ और सराहां उप-विभागों को शामिल करता है। यह क्षेत्र आड़ू और अन्य गुठली दार फलों के उत्पादन के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। स्थानीय लोग, जो मुख्य रूप से खश राजपूत कबीले से संबंधित हैं, स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभा चुके हैं। घाटी के लोग प्रगतिशील और मेहनती हैं, और भगवान शिव और देवी दुर्गा की उपासना के लिए प्रसिद्ध हैं।
Renuka Ji

English: Renuka Ji, located about 40 km from Nahan, is a significant religious and tourist destination. The Renuka Lake, an oval-shaped water body, is the main attraction, where boating is popular among visitors. According to legend, the lake was formed when Parashurama’s mother, Renuka, immersed herself in the water. The area hosts a major fair during Kartika Ekadashi, attracting thousands of pilgrims.
Hindi: रेणुका जी, नाहन से लगभग 40 किमी दूर स्थित, एक महत्वपूर्ण धार्मिक और पर्यटन स्थल है। रेणुका झील, जो अंडाकार आकार की है, मुख्य आकर्षण है और यहाँ नौकायन पर्यटकों के बीच लोकप्रिय है। किंवदंती के अनुसार, यह झील तब बनी जब परशुराम की मां रेणुका ने पानी में खुद को समाहित कर लिया था। इस क्षेत्र में कार्तिका एकादशी के दौरान एक बड़ा मेला आयोजित होता है, जो हजारों तीर्थयात्रियों को आकर्षित करता है।
Sarahan
English: Sarahan, the headquarters of Pachaad Tehsil and Development Block, is situated at an altitude of 1,668 meters. It offers panoramic views of the plains and Churdhar. Sarahan is about 35 km from Nahan and is well-connected by state highways. It has essential facilities like a rest house, hospital, post office, and schools. The area is known for its scenic beauty and historical significance.
Hindi: सराहाँ, पच्छाद तहसील और विकास खंड का मुख्यालय, 1,668 मीटर की ऊंचाई पर स्थित है। यह मैदानी इलाकों और चूडधार के सुंदर दृश्यों का अवलोकन कराता है। सराहाँ, नाहन से लगभग 35 किमी दूर है और अच्छे राज्य राज्यमार्ग से जुड़ा हुआ है। यहाँ विश्राम गृह, अस्पताल, डाकघर, और विद्यालय जैसी आवश्यक सुविधाएँ उपलब्ध हैं। यह क्षेत्र अपनी सुंदरता और ऐतिहासिक महत्व के लिए जाना जाता है।
Tourist Destinations in Sirmaur District
Churdhar
- Description: Churdhar is the highest peak of the Shivalik Range, standing at 11,965 feet. It offers panoramic views and is a popular destination for trekkers.
Renuka Ji
- Category: Religious
- Description: Renuka Lake is located in the Sirmaur district of Himachal Pradesh, at an altitude of 672 meters above sea level. It is known for its religious significance and scenic beauty.
Gurudwara Paonta Sahib
- Description: Gurudwara Paonta Sahib is a renowned Sikh shrine in the Sirmaur district. It is significant to the Sikh community as Guru Gobind Singh Ji, the tenth Sikh Guru, spent a part of his life here
Multiple choice questions
1. Which city was established by Raja Karm Prakash in 1621 CE?
A. Shimla
B. Nahan
C. Paonta Sahib
D. Rajgarh
Answer: B. Nahan
Explanation: Nahan city was established by Raja Karm Prakash in 1621 CE and is the headquarters of the Sirmaur district.
2. What is the height of the Churdhar peak?
A. 9,500 feet
B. 11,982 feet
C. 12,500 feet
D. 10,000 feet
Answer: B. 11,982 feet
Explanation: Churdhar is the highest peak of the Shivalik range at 11,982 feet.
3. What is the local name of Churdhar?
A. Churdhari
B. Churdhani
C. Chud-Chandani
D. Churda
Answer: C. Chud-Chandani
Explanation: Churdhar is commonly known as Chud-Chandani, which translates to “snow-capped peak” in local terms.
4. Which temple is dedicated to Chudeshwar Mahadev Shiva?
A. Shrigul Temple
B. Dundi Devi Temple
C. Rani Tal Temple
D. Bhuresh Temple
Answer: A. Shrigul Temple
Explanation: The Shrigul Temple at the base of Churdhar peak is dedicated to Chudeshwar Mahadev Shiva.
5. Where is the Jaithak Fort located?
A. Near Shimla
B. Near Paonta Sahib
C. North of Nahan
D. Near Rajgarh
Answer: C. North of Nahan
Explanation: Jaithak Fort is located about 19 km north of Nahan.
6. What historical event is associated with Jaithak Fort?
A. Battle between British and Gurkhas
B. Mughal invasion
C. Sikh Empire expansion
D. Rajput invasion
Answer: A. Battle between British and Gurkhas
Explanation: Jaithak Fort is historically significant for the battle fought between the British and Gurkhas in 1810.
7. Which peak is referred to as “the silent sentinel” and was used for guarding state boundaries?
A. Churdhar
B. Haripur Dhar
C. Shrigul
D. Jaithak
Answer: B. Haripur Dhar
Explanation: Haripur Dhar, with its ancient fort, was used to guard state boundaries and is referred to as “the silent sentinel.”
8. What is the primary purpose of the Gurudwara Paonta Sahib?
A. Educational center
B. Historical monument
C. Religious pilgrimage
D. Cultural festival
Answer: C. Religious pilgrimage
Explanation: Gurudwara Paonta Sahib is a significant religious pilgrimage site for Sikhs and Hindus.
9. Which river flows near Paonta Sahib?
A. Ganges
B. Yamuna
C. Ravi
D. Beas
Answer: B. Yamuna
Explanation: Paonta Sahib is situated near the Yamuna River.
10. What is the height of the Renuka Lake above sea level?
A. 500 meters
B. 672 meters
C. 800 meters
D. 1,000 meters
Answer: B. 672 meters
Explanation: Renuka Lake is situated 672 meters above sea level.
11. Which deity is associated with Renuka Lake?
A. Vishnu
B. Shiva
C. Parshuram
D. Durga
Answer: C. Parshuram
Explanation: The Renuka Lake is linked with the legend of Parshuram and his mother, Renuka.
12. What is the key feature of the TriLokpur site?
A. Historical fort
B. Sacred river
C. Famous temple
D. Fossil park
Answer: C. Famous temple
Explanation: TriLokpur is known for the famous Devi Bala Sundari temple.
13. What is the main attraction of the Sirmaur district’s fossil park?
A. Ancient temples
B. Historical artifacts
C. Prehistoric animal fossils
D. Natural landscapes
Answer: C. Prehistoric animal fossils
Explanation: The Sirmaur district’s fossil park is famous for displaying prehistoric animal fossils.
14. Where is the TriLokpur village located?
A. Near Shimla
B. Near Nahan
C. Near Paonta Sahib
D. Near Rajgarh
Answer: B. Near Nahan
Explanation: TriLokpur is situated 24 km southwest of Nahan.
15. Which town is known for its peach orchards in the Sirmaur district?
A. Paonta Sahib
B. Rajgarh
C. Haripur Dhar
D. Sirmaur
Answer: B. Rajgarh
Explanation: Rajgarh is known for its peach orchards and lush green valley.
16. What is the main purpose of the Shivalik Fossil Park?
A. Recreational activities
B. Scientific research and education
C. Agricultural development
D. Cultural festivals
Answer: B. Scientific research and education
Explanation: The Shivalik Fossil Park serves scientific, educational, and recreational purposes related to prehistoric life.
17. What is the significant feature of the Renuka Fair?
A. Music and dance performances
B. Historical reenactments
C. Food and crafts market
D. Pilgrimage and religious rituals
Answer: D. Pilgrimage and religious rituals
Explanation: The Renuka Fair is known for its religious significance, including pilgrimage and rituals.
18. What does the Jaithak Fort overlook?
A. Dada Har
B. Kyarada Doon
C. Shivalik Hills
D. Rajgarh Valley
Answer: B. Kyarada Doon
Explanation: Jaithak Fort offers a view of the Kyarada Doon and surrounding hills.
19. Which peak provides views of the Badri-Kedar and Sattlaj River valleys?
A. Churdhar
B. Haripur Dhar
C. Jaithak
D. TriLokpur
Answer: A. Churdhar
Explanation: Churdhar peak offers panoramic views including the Badri-Kedar peaks and the Sattlaj River valleys.
20. What does the Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s association with Paonta Sahib signify?
A. Administrative center
B. Educational institution
C. Historical residence
D. Religious significance
Answer: D. Religious significance
Explanation: Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s association with Paonta Sahib is significant due to its religious importance for Sikhs.
21. How far is the Haripur Dhar from Nahan?
A. 80 km
B. 106 km
C. 50 km
D. 75 km
Answer: B. 106 km
Explanation: Haripur Dhar is located approximately 106 km from Nahan.
22. What role did the ancient fort at Haripur Dhar play?
A. Trade hub
B. Defense against invaders
C. Cultural exchange
D. Administrative center
Answer: B. Defense against invaders
Explanation: The fort at Haripur Dhar was used to defend the region from invaders and to guard the state boundaries.
23. What is the height of the Sirmaur district’s historical city?
A. 500 meters
B. 672 meters
C. 397.7 meters
D. 1,000 meters
Answer: C. 397.7 meters
Explanation: Paonta Sahib, a significant location in Sirmaur, is situated 397.7 meters above sea level.
24. Which temple is associated with the local deity Shaya in the Rajgarh area?
A. Shrigul Temple
B. Bhuresh Temple
C. Renuka Temple
D. Bala Sundari Temple
Answer: B. Bhuresh Temple
Explanation: The Bhuresh Temple in Rajgarh is associated with the local deity Shaya.
25. What is the purpose of the museum in the Shivalik Fossil Park?
A. Display modern artifacts
B. Exhibit prehistoric fossils
C. Promote local arts
D. Provide entertainment
Answer: B. Exhibit prehistoric fossils
Explanation: The museum in the Shivalik Fossil Park exhibits fossils of prehistoric animals.
6. What is the primary attraction of the Shrigul Temple?
A. Ancient carvings
B. Large statue of Shiva
C. Scenic views from the temple
D. Historical inscriptions
Answer: B. Large statue of Shiva
Explanation: The Shrigul Temple is known for its large statue of Shiva, making it a significant attraction.
27. Which local deity is the Bhuresh Temple dedicated to?
A. Durga
B. Shiva
C. Vishnu
D. Parshuram
Answer: B. Shiva
Explanation: The Bhuresh Temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, a significant deity in the region.
28. What is the significance of Renuka Lake during the Renuka Fair?
A. It becomes a pilgrimage site
B. It is used for boating
C. It serves as a cultural venue
D. It hosts local sports events
Answer: A. It becomes a pilgrimage site
Explanation: During the Renuka Fair, Renuka Lake becomes a major pilgrimage site, drawing many visitors for religious purposes.
29. How does the Churdhar peak contribute to the local climate?
A. It causes heavy rainfall
B. It influences the local temperature
C. It prevents snowfall in the region
D. It moderates the weather
Answer: A. It causes heavy rainfall
Explanation: The height and location of Churdhar peak influence the local climate, often resulting in heavy rainfall in the region.
30. What makes the Jaithak Fort historically significant?
A. It was built by Mughal emperors
B. It was a site of a significant battle
C. It served as a royal palace
D. It was a trading post
Answer: B. It was a site of a significant battle
Explanation: Jaithak Fort is historically significant due to the battle fought between the British and Gurkhas.
31. In which area is the famous peach orchard located?
A. Paonta Sahib
B. Nahan
C. Rajgarh
D. Renuka
Answer: C. Rajgarh
Explanation: Rajgarh is well-known for its peach orchards, contributing to its agricultural reputation.
32. What type of fossils can be found in the Shivalik Fossil Park?
A. Marine fossils
B. Dinosaur fossils
C. Prehistoric animal fossils
D. Plant fossils
Answer: C. Prehistoric animal fossils
Explanation: The Shivalik Fossil Park is renowned for its collection of prehistoric animal fossils.
33. What is the altitude of the Gurudwara Paonta Sahib above sea level?
A. 397.7 meters
B. 672 meters
C. 500 meters
D. 1,000 meters
Answer: A. 397.7 meters
Explanation: Gurudwara Paonta Sahib is situated at an altitude of 397.7 meters above sea level.
34. What is the main role of the Renuka Fair?
A. Cultural celebration
B. Religious pilgrimage
C. Agricultural festival
D. Sporting event
Answer: B. Religious pilgrimage
Explanation: The Renuka Fair primarily serves as a religious pilgrimage event, attracting many devotees.
35. What significant event took place at Haripur Dhar during its history?
A. An architectural marvel was constructed
B. A famous battle was fought
C. A royal decree was issued
D. A major trade route was established
Answer: B. A famous battle was fought
Explanation: Haripur Dhar was significant for its historical battle, adding to its importance.
36. Which of the following is NOT a key feature of the Renuka Lake?
A. Scenic beauty
B. Boating facilities
C. Large Shiva temple
D. Historical inscriptions
Answer: D. Historical inscriptions
Explanation: Renuka Lake is known for its scenic beauty and associated Shiva temple, but not for historical inscriptions.
37. What kind of educational role does the Shivalik Fossil Park serve?
A. Art education
B. Scientific research
C. Cultural studies
D. Historical education
Answer: B. Scientific research
Explanation: The Shivalik Fossil Park plays a crucial role in scientific research and education regarding prehistoric life.
38. What is the height of the Churdhar peak in feet?
A. 10,000 feet
B. 11,982 feet
C. 12,500 feet
D. 9,500 feet
Answer: B. 11,982 feet
Explanation: Churdhar peak stands at 11,982 feet, making it the highest in the Shivalik range.
39. How does the Renuka Lake contribute to local mythology?
A. It is believed to have healing powers
B. It is associated with a local deity
C. It is linked to historical battles
D. It represents an ancient civilization
Answer: B. It is associated with a local deity
Explanation: Renuka Lake is linked to the local mythology involving the deity Renuka.
40. What is the altitude of the Churdhar peak in meters?
A. 3,500 meters
B. 4,800 meters
C. 5,000 meters
D. 6,000 meters
Answer: B. 4,800 meters
Explanation: The Churdhar peak stands at an altitude of 4,800 meters above sea level.
41. Which peak is known for offering views of the Badri-Kedar peaks?
A. Shrigul
B. Jaithak
C. Churdhar
D. Haripur Dhar
Answer: C. Churdhar
Explanation: The Churdhar peak provides extensive views, including the Badri-Kedar peaks.
42. What is a primary feature of the TriLokpur village?
A. Ancient ruins
B. A renowned temple
C. Natural hot springs
D. Historical fort
Answer: B. A renowned temple
Explanation: TriLokpur village is known for its significant temple, Devi Bala Sundari.
43. What kind of cultural events are held at the Renuka Lake during the fair?
A. Dance performances
B. Music concerts
C. Pilgrimage rituals
D. Food festivals
Answer: C. Pilgrimage rituals
Explanation: During the Renuka Fair, pilgrimage rituals are the primary cultural events held at the lake.
44. Which district is famous for its peach orchards?
A. Sirmaur
B. Shimla
C. Kangra
D. Mandi
Answer: A. Sirmaur
Explanation: The district of Sirmaur, particularly in Rajgarh, is renowned for its peach orchards.
45. Which historical site is known for its strategic location in Sirmaur?
A. Jaithak Fort
B. Renuka Lake
C. Churdhar Peak
D. Shrigul Temple
Answer: A. Jaithak Fort
Explanation: Jaithak Fort is known for its strategic location and historical importance in Sirmaur.
These questions cover a broader range of details and aspects related to the Sirmaur district and its attractions.